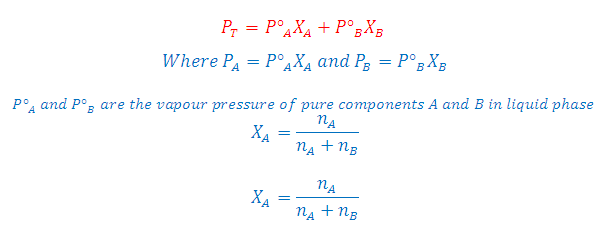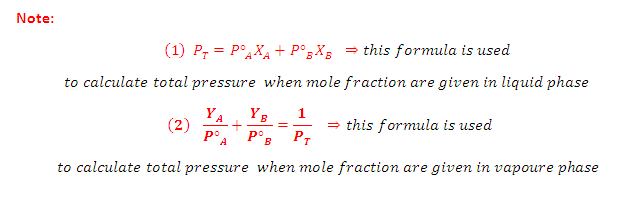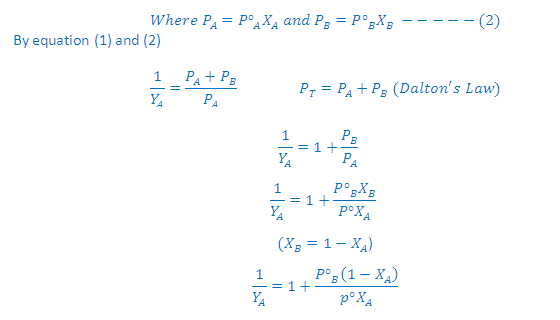VAPOUR PRESSURE:
(1) If a sample of water in its liquid phase is placed in an empty container, some of it will vaporize to form gaseous of water. This change is called evaporation.
(2) The pressure exerted by the vapour (molecules in the vapour phase) over the surface of the liquid at the equilibrium at given temperature is called the vapour pressure of the liquid.
OR
(3) It is the pressure exerted by the vapour when vapours are equilibrium with the liquid.
(4) The pressure exerted by vapours is called unsaturated vapour pressure or partial vapour at non equilibrium condition.
Factors affecting vapour pressure:
(A) Temperature:.
(1) The temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure is called its boiling point.
(2) Vapour pressure is directly proportional to theTemperature so that on increasing temperature the rate of evaporation increases and rate of condensation decreases and hence vapour pressure
increases.
(3) The dependence of vapour pressure and temperature is given by CLASIUS CLAPERON equation.
(4) Vapour pressure of a particular liquid system is only the function of temperature only. It is independent from all other factors like surface area, amount of liquid, available space etc.