Formation of
bridge bonds is properly explained by MOT.
According to which these bonds are formed
by filling electrons into molecular orbital’s which lies over three nuclei
hence such bonds are called specified as three centre bonds.
Bond angle between bridge bonds is less than bond angle between terminal bonds.
Bridge bonds are longer than
terminal bonds
Bond energy of 3C-2e bond is found to be higher than 2C-2e bond for same substitute. It may also be true for 4C-4e bond.
During formation of bridge bond empty atomic orbitals of central atom participate in hybridization.
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES (1):
ILLUSTRATIVE
EXAMPLE (2): BCl3 do not dimerised due to back
bonding
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (3): AlCl3 will
have also very less back bonding due to crowding
ILLUSTRATIVE
EXAMPLE (4): Steric crowding will
there in B(CH3)3
IMPORTANT NOTES:
(1) If there is no steric crowding and back bonding
in a molecules then bridge bond formed and molecules dimerised and stabilized
and dimerisation are more stable than back bonding.
(2) Most of the electron deficient compound attains
stability by performing back bonding or they undergo dimerisation provided
certain conditions are fulfilled
(3) BCl3 ,BBr3 BI3 and B(Me)3 although they are electron deficient compound but
do not undergo dimerisation because of steric factor in demmeric formed
TYPE
OF BRIDGE BOND:
(1) 3C-2e Bond Or Banana Bond
(2) 4C-4e Bond
(1) 3C-2e BOND OR BANANA BOND:
ILLUSTRATIVE
EXAMPLE (5): FORMATION OF B2H6:
(1) Formation of 3C-2e bond in B2H6
is best explain by MOT and total number of bond in B2H6
is 6 (3C-2e=2 and 3C-4e=4)
(2) Bridge bonds are
longer than terminal bond because at bridge bonds electrons are delocalized at
three centres
(3) Bond energy (441kj/mole) of B-H-B bond is
greater than bond energy (381 K j/mole) of B-H
bond.
(4) Hybridization of
B atom is sp3, so non planer, and non polar (U=0)
(5) B2H6 Methylated up to B2H2 Me4
(6) B2H6 is hypovalent molecule hence act as Lewis
acid and undergoes two type of cleavage when react with Lewis base:
(A)
UNSYMETRICAL CLEAVAGE:
B2H6 Undergo unsymmetrical cleavage with small size
strong Lewis base like NH3 NH2Me and NH (Me) 2 etc.
(B)
SYMETRICAL CLEAVAGE:
B2H6 undergoes symmetrical cleavage with large size
weak Lewis base like PH3, PF3,Me3N , OEt , OMe3, pyridine , THF , Thiophene , SMe2 ,Set2
(2) 3C-4e BOND or 3C-4e BRIDGE BOND:
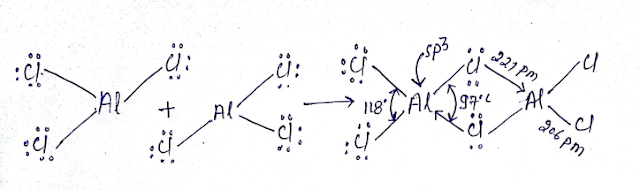
AL2Cl6
Dimmerised by 3C-4e bond bridge bond:
Al2Cl6 is neither hypovalent nor hypovalent rather
its octet is complete.
We will used MOT
here it cannot act as Lewis acid due to crowding in spite having vacant
d orbital’s however Alcl3
act as Lewis acid .
Al2Cl6
contains six bond having two bridge bond(3c-4e) and four bond is (2C-2e)
Boron
do not formed bridge bond because boron experience steric crowding.
REASON OF DIMERISATION:
(1) By formation of 3C-2e bond
(2) By formation of 3C-4e bond
(3) By pairing of unpaired electrons.
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (6): Which of the following molecule is/are dimerized by co-ordination bond?
(A)
AlCl3 (B)
BeCl2 (C)
ICl3 (D)
All of these
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (7):
The geometry with respect to the central atom of the
following molecules are: N (SiH3)3
; Me3N ; (SiH3)3P
(A) Planar,
pyramidal, planar
(B) Planar,
pyramidal, pyramidal
(C) Pyramidal,
pyramidal, pyramidal
(D) Pyramidal,
planar, pyramidal
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (8): Which one of the following statements is not true regarding diborane?
(A) It
has two bridging hydrogens and four perpendicular to the rest.
(B)When
methylated, the product is
(C)
The bridging hydrogens are in a plane perpendicular to the rest.
(D)
All the B–H bond distances are equal.
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (9): The structure of diborane (B2H6) contains
(A)
Four (2C–2e–) bonds and two (2C–3e–) bonds
(B)
Two (2C–2e–) bonds and two (3C–2e–) bonds
(C)
Four (2C–2e–) bonds and four (3C– 2e–) bonds
(D)
None of these
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (10): The molecular shapes of diborane is shown:
Consider
the following statements for diborane:
1.
Boron is approximately sp3 hybridized
2. B-H-B
angle is 180°
3.
There are two terminal B-H bonds for each boron atom
4.
There are only 12 bonding electrons available
Of
these statements:
(A)
1, 3 and 4 are correct (B) 1, 2 and 3
are correct
(C) 2,
3 and 4 are correct (D) 1, 2
and 4 are correct
Assertion & Reason:
ILLUSTRATIVE
EXAMPLE (11):
Statement-1
: BeH2 undergoes polymerisation while BH3 undergoes
dimerisation.
Statement-2
: After dimerization of BH3 molecules into B2H6,
no vaccant orbital at B
atom
isleft to carry on further polymerization. However, in case of BeH2,
after dimerization of BeH2molecules into Be2H4
each Be atom still contain sone empty 'p' orbital which brings further
polymerization.
(A)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is correct explanation
for statement-1.
(B)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is NOT the correct
explanation forstatement-1.
(C)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false.
(D)
Statement-1 is false, statement-2 is true.
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (12):
Statement-1:
The B–F bond length in BF3 is not identical with that in –BF4
Statement-2:
Back bonding is involved in –BF4 but not in BF3
(A)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is correct explanation
for statement-1.
(B)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is NOT the correct
explanation forstatement-1.
(C)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false.
(D)
Statement-1 is false, statement-2 is true.
ILLUSTRATIVE
EXAMPLE (13):
Statement-1:
(CH3)3Si – OH is more acidic than (CH3)3C
– OH.
Statement-2:
(CH3)3 Si – OH has back bonding.
(A)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is correct explanation
for statement-1.
(B)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is NOT the correct
explanation for statement-1.
(C)
Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false.
(D)
Statement-1 is false, statement-2 is true.
Answers
Key:












Amazing explanation! Haven't found anything better than this!
ReplyDeletejust awesome explanation,it helped me in neet preparation
ReplyDelete