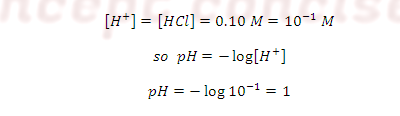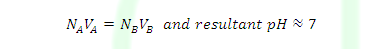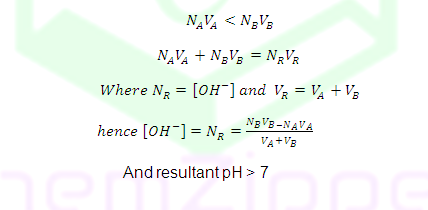Search This Blog
Showing posts with label IONIC EQUILIBRIUM:. Show all posts
Showing posts with label IONIC EQUILIBRIUM:. Show all posts
Friday, February 12, 2021
Saturday, September 26, 2020
The pH range of a basic indicator is 4 to 6.5 Calculate the dissociation constant of indicator?.
SOLUTION:
pKIn must be
midpoint of pH range for acidic indicators and pOH range for basic indicators
The pH range = 4 to 6.5 so pOH
range is 10 to 7.5
Hence PkIn = (10+7.5) /2 = 8.75
What are DOUBLE SALTS ?
DOUBLE SALTS:
(1)The addition compounds formed by the combination of
two simple salts are termed as double salts.
(2) Double salts are stable in solid state only.
(3) When dissolved in water, it furnishes all the ions
present in the simple salt form which it has been constituted.
(4)The solution of double salt shows the properties of
the samples salts from which it has been constituted
For examples
Mohar’s salt-FeSO4 (NH4)2SO4
.6H2O (Ferrous ammonium sulphate)
Alum’s- K2SO4Al2
(SO4)3. 24H2O (Potassium ammonium sulphate)
Karnalite-
KCl.MgCl2.6
(H2O)
Dolomite- CaCO3.MgCO3 or CaMg
(CO3)2
Topic:
IONIC EQUILIBRIUM:,
SALT HYDROLYSIS:
Wednesday, November 27, 2019
TITRATION OF STRONG ACID WITH STRONG BASE:
The titration of HCl (aq) with a
standardized NaOH solution illustrated the titration of strong acid by a strong
base.
The molecular and net ionic equation
is.
Case (1): At the start point before any titrant has
been added the receiving flask contains only 0.10 M HCl and 50 ml. Because it
is strong acid so
Case (2): After starting but before equivalent point.
Case (3): At equivalent point
Case (4): Before equivalent point
TITRATION SUMMARY TABLE:
|
S.N.
|
Volume of
HCl Taken
|
Volume
of NaOH
|
PH
|
|
|
1
|
50.0 ml (In ml)
And 0.10 M
|
0.0 (In ml)
And 0.10M
|
1.0
|
|
|
2
|
|
10
|
1.17
|
|
|
3
|
|
20
|
1.36
|
|
|
4
|
|
30
|
1.60
|
NAVA>NBVB
|
|
5
|
|
40
|
1.95
|
|
|
6
|
(Vertical Over)
|
45
|
2.27
|
|
|
7
|
|
49
|
2.99
|
|
|
8
|
50.0 ml (In ml)
And 0.10 M
|
50
|
7.0
|
NAVA=NBVB
|
|
9
|
|
51
|
11
|
NAVA<NBVB
|
|
10
|
|
60
|
11.95
|
|
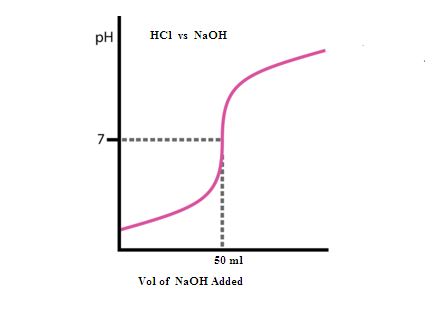
GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION:
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE: Find the pH of following titrations:
(A) 500 ml, 0.10 M HCl + 500 ml 0.10 M Ca(OH)2
(B) 400 ml, M/200 Ca(OH)2 + 400 ml M/50 HNO3
ANSWERS KEY:
(A): PH=12.6989 (B): PH=2.6
(A): PH=12.6989 (B): PH=2.6
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)