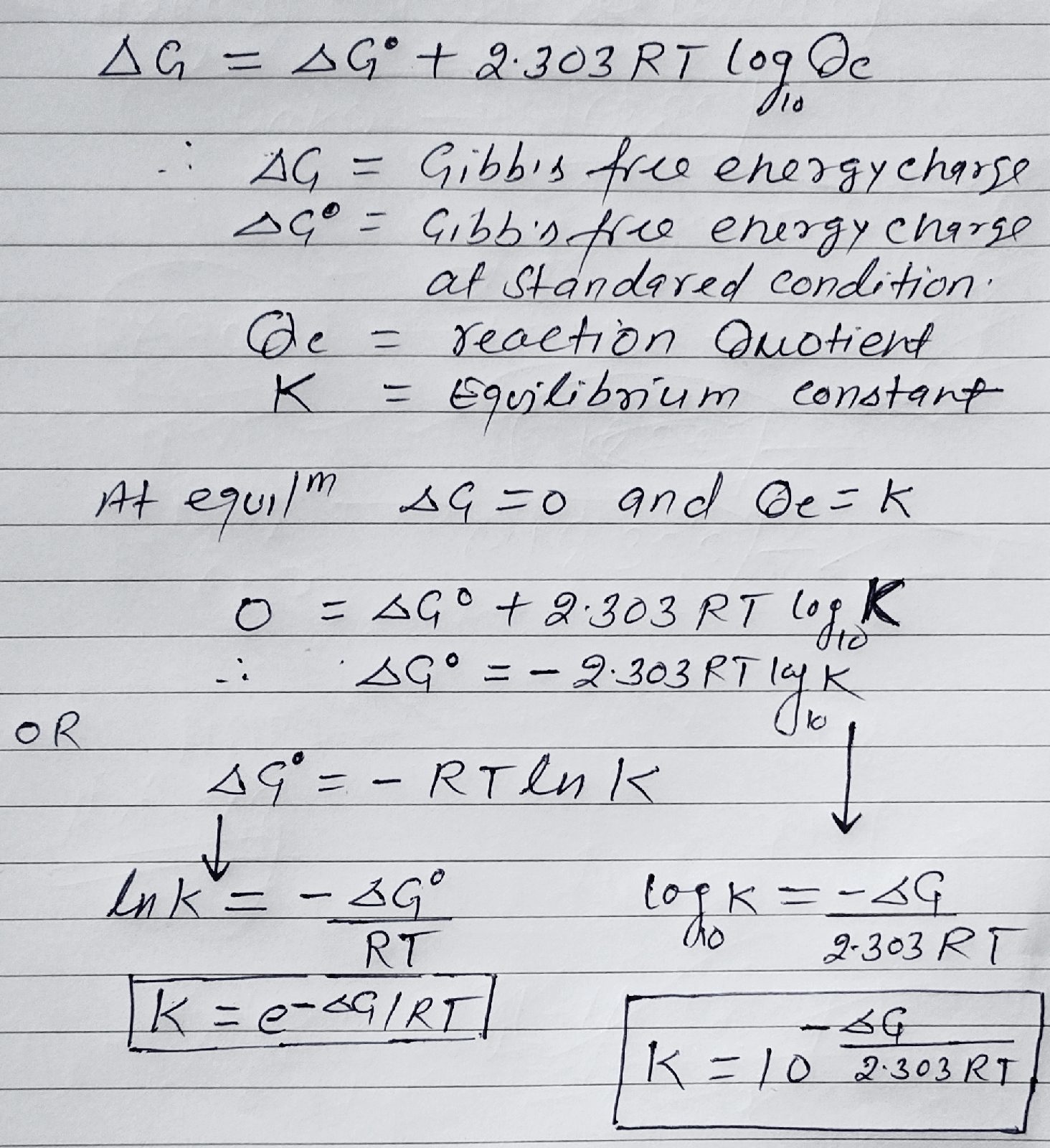Search This Blog
Showing posts with label CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:. Show all posts
Showing posts with label CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:. Show all posts
Sunday, September 10, 2023
ΔG^ o at 25^°C for the reaction 1/2N2(g) + 3/2H2(g) ⇋ 2NH3(g) is -11.392 kj mole^-1. Hence thermodynamics equilibrium constant is : he equilibrium constant for reaction is 10. (Use R=8.3 JK ^−1 mol ^−1)
Answer key : 10^2
The dissociation equilibrium of a gas AB2 can be represented as : 2AB2(g) ⇋ 2AB(g) + B2(g) The degree of dissociation is "x" and is small compared to 1. The expression relating the degree of dissociation (x) with equilibrium constant Kp and total pressure P is.
Friday, September 8, 2023
Relation between Kp and Kc:
When concentration are expressed in terms of mole fractions.
We know that partial pressure (P) = Mole fraction × Total pressure (Pt)
Thursday, September 7, 2023
Sunday, September 3, 2023
Equilibrium constant for the reaction given below is 2.0 × 10^-7 at 300 K. calculate standard Gibb's free energy change for the reaction PCl5 (g) --=--PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) also calculate standard entropy change if ∆H° = 28.40 Kj mole-1.
Saturday, September 2, 2023
Gibb's free energy (∆G) and Equilibrium constant (Kc):
The part f energy which is converted into usefull work called Gibb's free energy or Gibb's function.
Energy (H) = Useful work (G) + Non useful (TS)
We van not calculate absolute value of 'G' so we calculate change in Gibb's free energy.
∆G = ∆H -∆TS
∆G = ∆H - (∆TS + T∆S). ......(1)
Standard Gibb's energy (∆G°) change at standard condition is 1 bar and 298 K
∆G° = ∆H° -∆TS° .......(2)
Relation between ∆G° and Equilibrium constant (K):
Topic:
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:
Factor's Affecting Equilibrium Constant
(1) Le-Chetelier'e principle
(i) Effect of change in temperature
(ii) Effect of change in concentration
(iii) Effect of change of volume of container at equilibrium
(iv) Effect of change in pressure
(v) Effect of Catalyst at equilibrium
(vi) Effect of Addition of Inert gas
(a) At constant volume
(b) At constant pressure
[End of Chapter = ∆∆∆]
Topic:
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:
Application of Equilibrium Constant (K):
(1) Predicting extent of reactions
(2) Predicting of stability of reactants and products
(3) Predicting direction of reactions at any instant of reaction (Qc)
(4) Predicting concentration of reactants and products at equilibrium.
(5) Degree of dissociation and Kp and Kc in term of DOD.
(6) Degree of dissociation and Vapour density.
Topic:
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:
Tuesday, August 29, 2023
Relation between Kp and Kc and Law of Mass of action: Equilibrium constants:
LAW OF MASS ACTION: Law of mass action is applicable for only reversible chemical reactions and it is an imperial law.
The law state that “ At a fixed temperature the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of reactive mass of reactants raised to the their respective Stoichiometric coefficients ” The law of mass action is by Guldberg and Waage.
(1) Equilibrium Constants in term of concentration ( KC):
At the constant temperature, let us consider the following reversible reaction

According to law of mass action - The rate of forward reaction
The rate of reverse reaction-
Where Kf and Kb is the rate constant of the forward reaction and backward reaction respectively
We know at equilibrium, the two rates of forward as well as backward are equal. ie
Rate of reaction = Rate of forward reaction – Rate of backward reaction = 0
Kc=Kf/Kb
Unit of Kc= (Conc)ng
(2) Equilibrium Constants in term of Pressure( Kp):
From law of mass action- rate forward reaction is directly proportional to product of active mass of reactants and

For an ideal gas PV=nRT
Where
P= Pressure in atm
V=Volume in liters
n=Number of gaseous moles
R=Gas constant
= 0.0821 L atm/mol/K or 1/12 L atm /mole/K
T=Temperature in kelvin
= total number of moles of gaseous products -total number of moles of gaseous reactants

Illustrated examples:
The value of Kc for the reaction (formation of ammonia by haber process) is 0.50 at 400º C.What will be the value of Kp at 400ºC when concentration are expressed in mole litre.1 and pressure in atmosphere ?
Methanol (CH3OH) is manufactured industrially by the reaction CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) The equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction is 10.5 at 220°C. What is the value of Kp at this temperature ?
SOLUTION: Give Data ,Kc = 10.5 ,T= 220oC = (220 + 273)K = 493 K

Relation Between vapour density and degree of dissociation : Theory and Numericals:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)