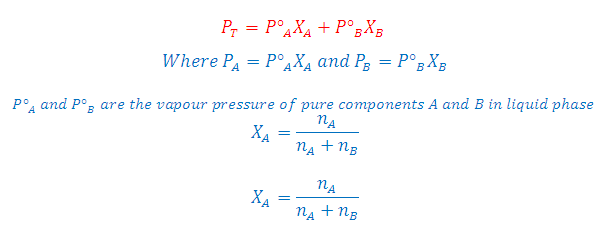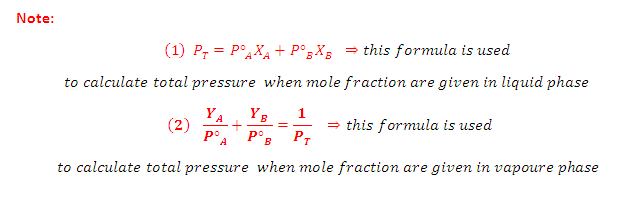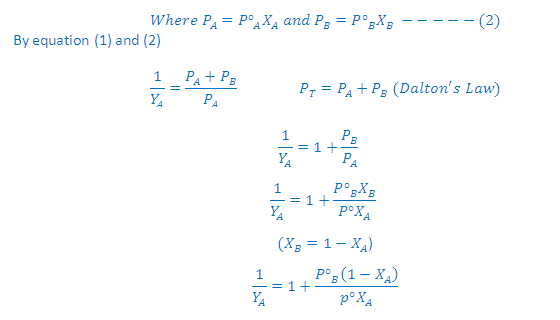Search This Blog
Wednesday, May 3, 2023
Henry`s law is not applicable for the aqueous solution of.......
Thursday, September 29, 2022
Van’t Hoff Factor
Colligative Properties
These are the properties that depend on the concentration of solute molecule or ions in solution but not on the chemical identity of the solute.
For example, addition of ethylene glycol to water lowers the freezing point of water below 0°C.
The magnitude of freezing point lowering is directly proportional to the number of solute molecules added to a particular quantity of solvent.
(1) If 0.01 mole of ethylene glycol is added to 1 kg of water, the freezing point is lowered to - 0.019°C while
(2) On adding 0.020 mole of ethylene glycol to 1 kg of water, the freezing point is lowered to -0.038°C.
The various colligative properties are
(1) Relative lowering of vapour pressure
(2) Osmotic pressure
(3) Elevation of boiling point
(4) Depression of freezing point
If N2 gas is bubbled through water at 293 K, how many millimoles of N2 gas would dissolve in 1 litre of water. Assume that N2 exerts a partial pressure of 0.987 bar. Given that Henry’s law constant for N2 at 293 K is 76.84 kbar.