(1) Polydentate ligands :
have Flexi dentate character, it is not necessary that all the
donor atoms present in the Polydentate ligands should form coordinate bonds with
central metal atom or ion.
(2) Ambidentate Ligands: Ligands which
can ligate through two different atoms present in it are called Ambidentate
ligands. Examples of such ligands are the NO2, and SCN ions. NO2
, ion can coordinate through either the nitrogen or the
oxygen atoms to a central metal atom/ion. Similarly, SCN¯ ion can coordinate
through the sulphur or nitrogen atom. There are certain ligands which have two
or more donor atoms but during formation of complexes only one donor atom is
attached to metal ion. Such ligands are called Ambidentate ligands such as CN¯,
CNS¯
(3) Chelating ligands:
(1) Polydentate ligands whose structures
permit the attachment of two or more donor sites to the same metal ion simultaneously,
thus closing one or more rings are called chelating ligands and the compounds formed are
known as chelate compounds.
(2) A chelate may be defined as a ring
structure formed by the combination of a Polydentate ligand having two or more
donor atoms with a metal ion forming part of the ring.
(3) The process of formation of chelates
is called chelation.
(4) Chelate complexes are more stable
than ordinary complexes in which the ligand is a monodentate
(5) This increased stability of the
compound due to chelation is called the chelate effect
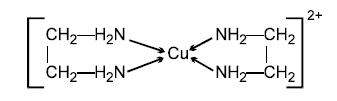
(6) In the complex ion given below,
5membered rings are formed. So all these are called chelate complexes
(9) Generally the chelate complexes with 5 or 6 membered
rings are more stable.
(10) Out of these, 5 membered rings are very stable
when they involve saturated ligands.
(11) On the other hand 6-membered ring
structures acquire maximum stability when they involve unsaturated ligands
containing conjugate double bond. This is due to the resonance effects
involving metal d-orbitals and ligand p-orbital electrons.
IllUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (1): Match the Column
A and B
|
|
Column A
|
|
Column B
|
|
(1)
|
Ligand
contains one donor site
|
(a)
|
hexadented
|
|
(2)
|
Ligand
contains two donor site
|
(b)
|
tridented
|
|
(3)
|
Ligand
contain three donor site
|
( c)
|
tetradented
|
|
(4)
|
Ligand
contain four donor site
|
(d)
|
bidented
|
|
(5)
|
Ligand
contain six donor site
|
(e)
|
unidented
|
SOLUTION: (1)
- (e); (2) - (d); (3) - (b); (4) - (c); (5) - (a)

No comments:
Post a Comment