Silicon is unable to form pp -
pp bond with oxygen atom due to its relatively
large size. Thus it satisfies its all four valency with four oxygen atoms and
constitutes three - dimensional network. In this
structure each oxygen atom is shared by two silicon atoms. Three
crystalline modification of SiO2 are quartz, cristobalite
and tridymite of which quartz and cristobalite
are important.
Quartz (rock crystal) is the purest form of silica. It is used in
preparation of costly glasses and lenses. It is also used as piezoelectric material (crystal oscillators and
transducers).
Several
amorphous forms of silica such as silica gel and fumed silica are known. Silica
gel in made by acidification of sodium silicate and when dehydrates, is
extensively used as a drying agent in chromatographic and catalyst support.
STRUCTURE OF SILICA:
PREPARATION OF SILICA:
Artificially
silica can be obtained by following methods
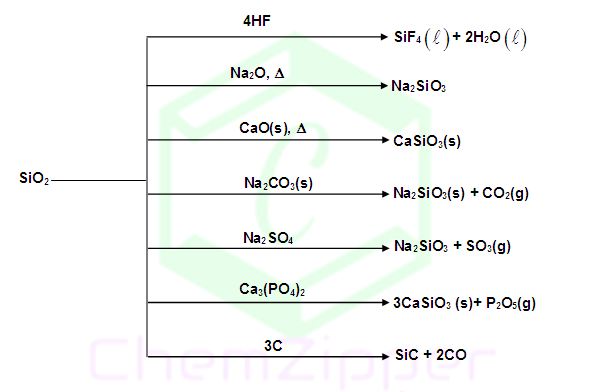
PROPERTIES OF SILICA:
Pure
silica is colourless but sand is brownish or yellowish due to presence of
impurities of iron oxide.
Question: Why SiO2 is solid while CO2
is a gas?
Answer: This is because SiO2 exists in silicate
form where Si forms tetrahedron SiO42- ions which are
regularly attached with each other and form a giant network structure hence
remains solid.



No comments:
Post a Comment