It is equal to number of modes of energy transfer when a gaseous molecule undergoes collision. OR
It represent the number of independent modes to describe the molecular motion.
Total degree of freedom = 3N (Where N is Number of atom in molecule)
Total degree of freedom = 3N (Where N is Number of atom in molecule)
1- Translational degree of freedom is 3 (three) always for mono, di and t tri atomic molecule.
2- Rotational degree of freedom is zero for mono atomic gas, 2 (two) for diatomic molecules and 3 (three) for triatomic molecule
3-Vibrational degree of freedom is also zero for mono atomic gas and 1(one) diatomic gas molecule and for polyatomic gases Vibrational DOF is calculated individually.( fvib= 3N- ftrans+ frot)
Total degree of freedom:= ftrans + f rot + f vib & fvib= 3N- ftrans + f rot
Molecules N TDF
He 1 3
O2 2 6
CO2 3 9
NH3 4 12
PCl5 6 18
Case-1
Monoatomic Diatomic Triatomic (linear) Triatomic (Non linear)
f total =3 ftotal =6 ftotal =9 f total=9
f trans=3 ftrans =3 ftrans=3 ftrans=3
f rot =0 frot =2 frot = 2 frot =3
f vib =0 fvib =1 fvib = 4 fvib =3
q =n CmdT
qV=n CvmdT
(Cm)v=(dq/dT)v
By FLOT dq= dU+ dW
At constant volume dW=0 so dqv=dU
Hence (
LAW OF EQUIPARTIAL OF ENERGY :
Average energy associate with each molecule per degree of freedom is U= 1/2KT (where K is Boltz’s man constant.
Average energy associate with each molecule per degree of freedom is U= 1/2KT (where K is Boltz’s man constant.
Let degree of freedom is = f then U is U=1/2fkT
And U=1/2fkTNA per molecule we know kNA=R
U=1/2fRT and dU/dT=1/2fR
And dU/dT=Cv hence Cv=1/2fR
Cv=1/2ftransR +1/2frotR (Where Vib degree inactive in chemistry)
For ideal gas Cpm-Cvm=R and Gama= Cpm/Cvm
Adiabatic exponent :Adiabatic exponent (Gama) for a mixture of gas with different heat capacity is defined as :
where n1, n2 ........................ are moles of different gases
Example: Calculate change in internal energy of 10 gm of H2 ,when it's state is changed from(300K, 1Atm) to (500 K, 2Atm) ?
Solution: For ideal gas
Cv for H2 (diatomic) in low temperature range will be 5R as vibrational part is not included.


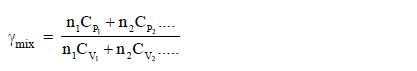

No comments:
Post a Comment