Nucleaphilic
substitution reactions, at the minimum
H-(hydride) ion from aldehydes and -CH3 from ketones needs to be
withdrawn. These are strong nucleophiles, and can not be displaced by other
nucleophiles, therefore, carbonyl compounds can not undergo nucleophilic
substitution reactions.
Search This Blog
Showing posts with label REACTION MECHANISM:. Show all posts
Showing posts with label REACTION MECHANISM:. Show all posts
Wednesday, January 29, 2020
Only aldehydes, methyl ketones and cyclic ketones react wilh sodium bisulphite.explain why?
Due
to the larger size at sulphite ion, it can attack only those carbonyl
compounds. where, there is lesser sterie hinderance, that's why, it
reacts with only aldehydes, methyl ketones and cyclic ketones.
Why does benzene undergoes substitution reaction instead of addition reaction?
Benzene nucleus present
in all the aromatic hydrocarbons is very stable; it gives a number of
substitution reactions but resists addition reactions. Benzene also fails to
give tests for unsaturation i.e. it does not decolourise alkaline KMnO4 and
bromine water.
Benzene gives electrophilic substitution due to It is
due to the following reasons:
(2) Due to the presence
of π-electron cloud above and below the plane of carbon atoms of the benzene
ring.
(2) Benzene ring acts as
a source of electrons for electrophilic reagents.
(3) In electrophilic substitution
aromatic character of benzene ring is preserved due to resonance
stabilisation. The formation of formation of addition product
will destroyed the aromatic ring structure of benzene and therefore
addition takes place with very difficulty. On the above explanation we can say
that electrophilic substitution reactions are feature of benzene ring.
Sunday, January 26, 2020
Give the products formed on heating of 1,1,2-cyclohexane tricarboxylic acid.
First Geminal acid on heating undergo decarboxylation to formed 1,2-Cyclohexane Dicarboxylic acid, which is on further heating gives corresponding anhydride.
Related Questions:
Friday, January 24, 2020
What is fries rearrangment acylation ?
Conversion of phenolic esters of aliphatic and aromatic carboxylic acids into ortho- and para-acylphenols in the presence of FCR catalyst (AlCl3). Is know as Fries rearrangement.
Related questions:
What is difference between Houben–Hoesch acylation reaction and Gatter- mann–Koch formylation reaction?
Related questions:
What is difference between Houben–Hoesch acylation reaction and Gatter- mann–Koch formylation reaction?
More reated Questions:
What is difference between Houben–Hoesch acylation reaction and Gatter- mann–Koch formylation reaction?
Houben–Hoesch reaction ia an analogous reaction of Gatter-mann–Koch reaction, it is sometimes called the Hoesch reaction.
Houben–Hoesch reaction:
Hoesch reaction is basically FACT acylation of aromatic compounds with nitriles and HCl.
Gatter-mann–Koch reaction:
Gatter-mann–Koch reaction is formulation of benzene ring in the presence of CO and HCl.
How write mechanism of exhaustive methyl and Hoffmann elimination of ethanamine?
Related Questions:
(2) Write Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism
of 1-cyclobutylethanol in the presence of con H2SO4.
What is mechanism of exhaustive methylation and Hoffmann elimination of piperidine a secondary amine?
This reaction can be used to determine the structure of amines especially in complex molecules such as alkaloids.
Related Questions:
Explain Exhaustive alkylation and Hoffmann Elimination.
Then reaction of amines with excess of alkyl halides to form a quaternary ammonium salt is known as exhaustive alkylation and if the alkyl group is methyl, then it is known as exhaustive methylation .
The exhaustive methylation of amine followed by treatment with moist silver oxide (AgO + O2--> AgOH) and subsequent heating to form alkene is known as Hoffmann elimination.
Related Questions:
(2) Write Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism
of 1-cyclobutylethanol in the presence of con H2SO4.
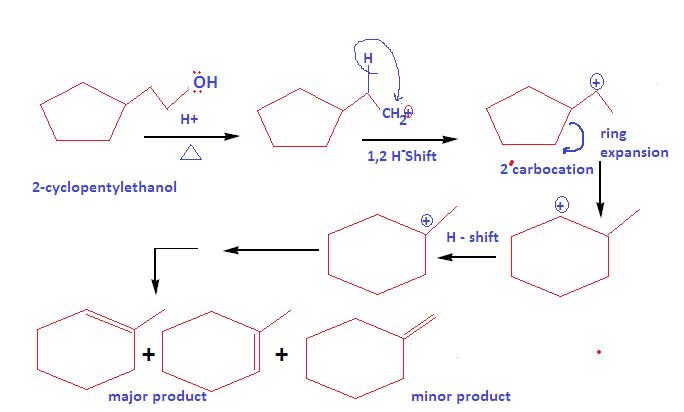
(6) How to write dehydration and
ring expansion mechanism of 2-cyclopentylethanol?
(7) Write the major and minor product of hydration of 1-Methylcyclopent-1-ene in acidic medium?
(7) Write the major and minor product of hydration of 1-Methylcyclopent-1-ene in acidic medium?
Thursday, January 23, 2020
Monday, January 20, 2020
How to prepare p-bromoaniline, knowing that aniline only gives the tris-brominated product; note that bromination of aniline does not stop at the monobrominated stage and cannot be moderated by using only one equivalent of bromine.
SOLUTION:
Moderating the activity of NH2 by
reacting of aniline with acetic anhydride
The activating influence of NH2 has
been reduced due to competing withdrawal of N-lone pair by carbonyl group:
Related Questions:
- Why do not Friedel-Crafts reactions succeed on aromatic rings that are substituted either by a strongly electron-withdrawing group such as carbonyl (C=O) or by an amino group (-NH2, NHR, -NR2):
- Why does not aniline undergo Friedel crafts reactions explain?
- Why Friedel–Crafts alkylations often give polysubstitution products but Friedel–Crafts acylations do not.
Thursday, January 16, 2020
How can write dehydration mechanism of 1,2,3-Trihydroxymethylcyclopropane into Benzene in acidic medium?
Mechanism:
The dehydration of “1,2,3-Trihydroxymethylcyclopropane” in acidic
medium follow E1 elimination mechanism . After performing E1 thrice it was expecting that the major product
is Benzene.The steps wise mechanism written through
carbocation formation and simple dehydration is given as below.
Related Questions:
Saturday, January 11, 2020
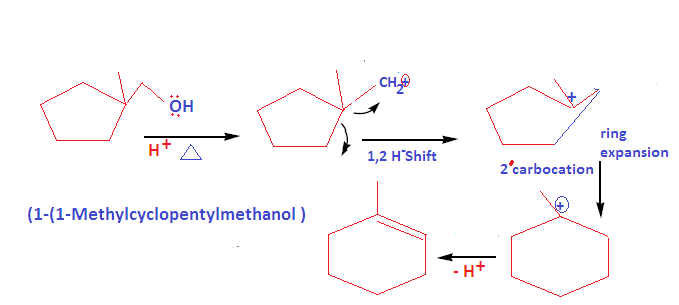
How to write dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 1-(1-cyclopentyl) methanol?
This mechanism proceed via carbocation formation and ring expansion mechanism:
Related Examples:
How to write dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of Tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol?
This mechanism proceed via carbocation formation and ring expansion mechanism:
Related Questions:
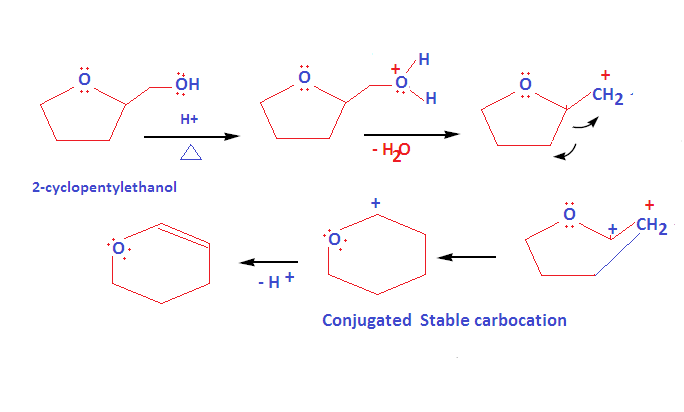
How to write dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 2-cyclopentylethanol?
This mechanism proceed via carbocation formation and ring expansion mechanism:
Explain Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 1-(1-Methylcyclopentyl)ethan-ol?
Write Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 1-cyclobutylethanol in the presence of con H2SO4.
Friday, January 10, 2020
Why do not Friedel-Crafts reactions succeed on aromatic rings that are substituted either by a strongly electron-withdrawing group such as carbonyl (C=O) or by an amino group (-NH2, NHR, -NR2):
We Know that acyl groups or any electron
withdrawing group present at ring which deactivating as result further
substitution does not take place
While in
case of Aniline or its derivatives, the Friedel Craft reaction
occurs in the presence of aluminium chloride which
is Lewis acidic and the Aniline is a strong base.
Therefore, when aniline is reacted with aluminium chloride in Friedel-Craft’s
reaction, formation of salt takes place. On which the presence of positive charge on nitrogen deactivates the benzene ring towards
electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Therefore, aniline does not
undergo Friedel-Craft’s reaction
Similar
Questions:
Why does not aniline undergo Friedel crafts reactions explain?
We know that
the Friedel Craft reaction occurs in the presence
of aluminium chloride which is Lewis acidic and
the Aniline is a strong base. Therefore, when
aniline is reacted with aluminium chloride in Friedel-Craft’s reaction,
formation of salt takes place. The salt
formation take place as:
The presence
of positive charge on nitrogen deactivates the benzene
ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Therefore, aniline
does not undergo Friedel-Craft’s reaction.
Similar
Questions:
Why Friedel–Crafts alkylations often give polysubstitution products but Friedel–Crafts acylations do not.
Write the Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of following alcohol:
This reaction proceed via carbocation
intermediate formation and ring expansion in which a molecule of water is lost in presence of concentrate
Sulphuric acid. The initially formed primary
carbocation rearranges to more stable secondary
carbocation which results in ring expansion.
Related Examples:
Explain Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 1-(1-Methylcyclopentyl)ethan-ol?
Explain the ring expansion mechanism of Bicyclic 1,2-Diols which undergoes pinacol pinacolone mechanism?
Write Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 1-cyclobutylethanol in the presence of con H2SO4.
Thursday, January 9, 2020
Write Dehydration and ring expansion mechanism of 1-cyclobutylethanol in the presence of con H2SO4.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)