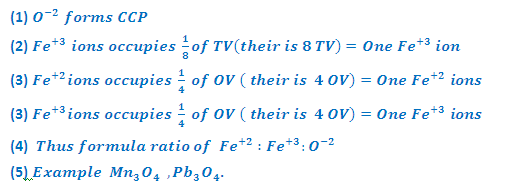INVERSE SPINEL STRUCTURE (Fe3O4-Magnetite):
Search This Blog
Saturday, November 28, 2020
What are the inverse spinel structures?
What are the normal spinel structures?
NORMAL SPINEL (AB2O4 )
STRUCTURE:
Example of Spinel is a MgAl2O4.( mineral) In it oxide ions (O-2) are arranged in ccp with Mg+2 ions occupying tetrahedral voids and Al+3 ions in a set of octahedral voids.
Many ferrites (such as ZnFe2O4) also possess spinel structure. These are very
important magnetic materials and are used in telephone and memory loops in
computers.
Sunday, June 14, 2020
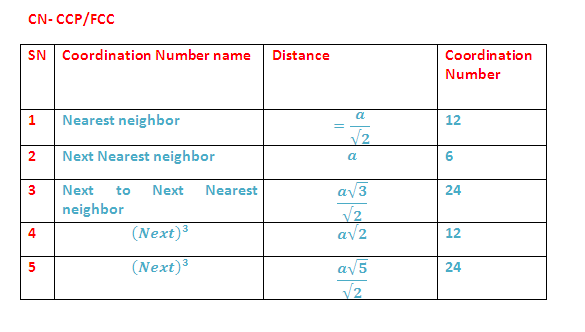
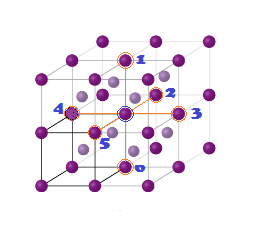
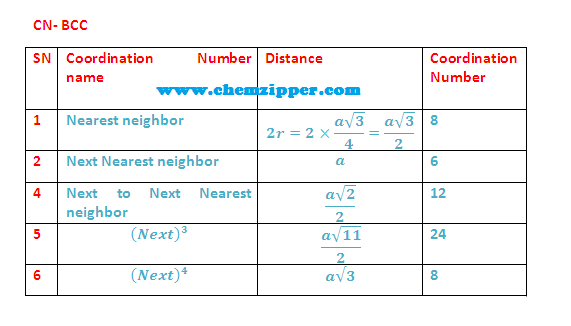
What are different stacking pattern of atoms in simple cubic cell (SCC) , body cubic cell (BCC) and face centred cell (FCC) unit lattice cell ?
"AA AA AA...", the letters refer to the repeating order of the layers, starting with the bottom layer.
"AB AB AB ..." Type of stacking pattern present a in body centred cubic (BCC).The considerable space shown between the spheres is misleading: spheres are closely packed in bcc solids and touch along the body diagonal.
"ABC ABC ABC..." type of stacking pattern is of face centered cubic (fcc) or cubic close packing (ccp) type.
Saturday, June 6, 2020
What is the effect of temperature and pressure on crystal structure of Caesium Chloride?
760 K, the CsCl type crystal structure having coordination 8:8 changed to NaCl type crystal structures having coordination 6:6.
What is the number of atoms on one unit cell of HCP?
Find the ratio of Fe+3 and Fe+2 in a non Stoichiometric oxide of iron , formulated as Fe_0.90 S_1.0 .
If the total number of atoms per unit cell in an hcp structure and a bcc structure gets halved, then ratio of percentage voids in hcp and bcc structures is
Sunday, May 24, 2020
If silver iodide crystallizes in a zinc blende structure with I- ions forming the lattice then calculate fraction of the tetrahedral voids occupied by Ag+ ions.
Saturday, May 23, 2020
A metal crystallizes into two cubic phases, face centered cubic (fcc) and body centered cubic (bcc), whose unit cell lengths are 3.5 A° and 3.0 A°, rcspcctively. Calculate the ratio of densities of fcc and bcc. (IIT-JEE 1999)
A metallic element crystallizes into a lattice containing a sequence of layers ABABAB....Any packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What percentage by volume of this lattice is empty space? ( IIT-.IEF 2006)
The coordination number of Al in the crystalline state of AlCl3 is .... (IIT-JEE 2009)
The number of hexagonal faces that are present in truncated octahedron is .... (IIT-JEE 2011)
What are structural information of Dimomd ?
Diamond structure
is ZnS type structure in which carbon
atoms forms a face centred cubic (FCC/CCP) lattice
as well as four out of eight
(50%) or alternate tetrahedral voids are
occupied by carbon atoms. Every atom in this structure is surrounded
tetrahedrally by four other. No discrete molecule can be discerned (identified)
in diamond .the entire crystal is giant molecule a unit cell of which is shown
as below.
Note
: Only those atoms which
form four covalent bond produce a repeated 3D structure using only covalent
bonds.
Lattice of Diamond is ZnS type structure.
(1) C- form FCC/CCP (4-atoms)
(2) C- atoms present at the (50%) alternative
tetrahedral voids (4-atoms)
(3) Total Number of one lattice unit is
eight (8) hence molecular formula of diamond is (C8) (i.e. Z= 8)
(4) Number of C-C bond in lattice cell
is = 4×4= 16
(5) Number of C-C bond per carbon atom
is 16/8=2
(6) The distance between two Corbin atom is dC-C = a√3/4 and the radius of carbon atom = dc-c/2 = rc = a√3/2x4
(8) Packing efficiency (PE = π√3/10= 0.34 or 34%):
(9) Voids = 66 %
Additional
Information: