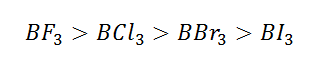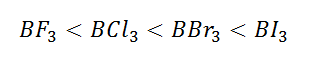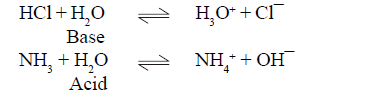SOLUTION: Sulphide ion (S2-) is less basic than oxide ion (O2-) due to its larger size. the oxide ion has a higher charge density than the sulphide ion hence the small H+ more attracted toward smaller ion (O2-) .
Search This Blog
Monday, January 11, 2021
Which is more basic oxide ion (O-2 ) or hydroxide ion( OH- ) and why ?
SOLUTION: The basic strength of base primarily depends on the ability of a species to attract H+, which is also depends upon electrostatic interactions. The smaller and more highly charged a negative species is, the stronger the attraction for the small, positive H+ ion. For example, O2- has a higher negative charge than OH-, and as a result it is a stronger base. One does not normally expect reactions that take place in aqueous solutions to produce oxides as a result of the basicity of O2-. Ionic oxides normally react with water to produce hydroxides:
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
Tuesday, December 29, 2020
The Usanovich Acid- Base Concept
According to this concept acids are any chemical species which react with bases and gives cations or accept anions or electrons.
Similarly Bases are a chemical species which react with acids and gives anions or electrons or cations
Hard and Soft acids and bases:
Lux- Flood Acid-Base Concept:
The Lux-Flood concept is given by Lux in 1929 and supported by Flood in 1947. Lux-Flood concept is based on oxide ion acceptor and donor tendency.
Lux-Flood bases: According to this concept bases are
those species which can donate oxide ions examples.
Lux-Flood Acids: According to this concept Acids are
those species which can accept oxide ions.
Chemical Reactions according Lewis acid-base concept:
Acid-base reaction in term Lux-Flood acid and base is a specific reactions in which oxide ions are mainly use in molten form or at high temperature.
Amphoteric Nature of Oxides as per Lux-Flood Concept:
Acidic Nature of Xenon
fluoride as per Lux-Flood Concept:
According to Lux –Flood concept Xenon
fluorides accept oxide ions from other compounds and insert fluorides ions in
its place.
For examples
The Order of decreasing Lux-Flood acidity of Xenon Fluorides is given as:
Limitations of Lux-Flood Acid –base Concept:
(1) It is
dealing with anhydrous reaction in fused molten oxides and other high temperature reactions found in
metallurgy and ceramics.
(2) When
Lux-Flood, acidic and basic of oxide react with water gives corresponding acid
and base.
Limitations of Lux-Flood Acid
–base Concept:
(1) Base
must contain oxide ion and acid must have accept oxide ions.
(2)It
fails to explain reaction without metal
ions
The Solvent system(Self or Auto Ionization of Solvents)
The most common concept of
acids and bases is due to Cady and Elsey. Most of the solvents undergo
auto-ionization and form cation and anions like water, regardless it contains
protons or not for examples; H2O, NH3, H2SO4, HNO3, POCl3,
BrF3, N2O4, NOCl, CH3COOH,
Related Questions:
Why aqueous solution of AlCl3 is acidic in nature ?
What happen when aq AlCl3 react with Acid or Base?
Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
Why BF3 do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter than B-F bond length in (BF4)- why?
What is product of reaction between diborane (B2H6) and ammmonia (NH3)?
Why methylation of Diborane (B2H6) replace four hydrogen only ?
What is use of Orthoboric acids?
What is basicity of "Boric acid" ?
Why Boric acid exist in solid state ?
What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
What is effect of heat on Borax?
What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
What is the Sodium per borate ,give the structure and its uses?
Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
What is the molecular formula of Borax ?
Why Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
Four-center two-electron bond (4C-2e Bond): Structure of AlCl3:
Sunday, December 27, 2020
Why is BCl3 a strongerLewis acid than BF3 ?
The strength of a Lewis acid is a measure of its ability to attract a pair of electrons on a molecule that is behaving as a Lewis base. Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine, so it appears that three fluorine atoms should withdraw electron density from the boron atom, leaving it more positive.This would also happen to some extent when the peripheral atoms are chlorine, but chlorine is less electronegative than fluorine. On this basis, we would expect BF3 to be a stronger Lewis acid. However,in the BF3 molecule, the boron atom uses sp2 hybrid orbitals, which leaves one empty 2p orbital that is perpendicular to the plane of the molecule. The fluorine atoms have filled 2p orbitals that can overlap with the empty 2p orbital on the boron atom to give some double bond character (Back Bond) to the B–F bonds.

As a result of the contribution by resonance structures having some double bond character, the boron atom in BF3 is not as electron deficient as it is in BCl3. And hence BCl3 a stronger Lewis acid than BF3
Monday, December 21, 2020
What are the order of extent back bonding, Lewis acid character and nucleophilicity of (BF3, BCl3, BBr3, BI3)boron trihalides?
(1) Back bonding extent in boron tri halides decreases from
BF3 to BI3 because on increasing of size of
p-orbital of halogens atom the strength of back bond decreases thus extent of back bonding:
Hence it is clear that BF3 is weakest Lewis acid
due to stronger 2pπ-2pπ back bonding (stronger partial double bond character)
in BF3 (lone pair orbital of fluorine into vacant orbital of
boron) and consequently behaves as less electron deficient. The back bonding
gradually decreases (From BF3 to BI3) and becomes
weakest in BI3. So that BI3 become strong Lewis acid
(3) The nucleophilicity(affinity towards nucleophile/water) order is
inversely proportional to the Lewis acid character thus
the nucleophilicity order is:
Related Questions:
Why aqueous solution of AlCl3 is acidic in nature ?
What happen when aq AlCl3 react with Acid or Base?
Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
Why BF3 do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter than B-F bond length in (BF4)- why?
What is product of reaction between diborane (B2H6) and ammmonia (NH3)?
Why methylation of Diborane (B2H6) replace four hydrogen only ?
What is use of Orthoboric acids?
What is basicity of "Boric acid" ?
Why Boric acid exist in solid state ?
What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
What is effect of heat on Borax?
What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
What is the Sodium per borate ,give the structure and its uses?
Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
What is the molecular formula of Borax ?
Why Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
Four-center two-electron bond (4C-2e Bond): Structure of AlCl3:
Thursday, June 25, 2020
Arrange the silicon halides into decreasing order of Lewis acids Character? SiF3, SiCl3, SiBr3, SiI3
Sunday, February 9, 2020
Why thionyl chloride behaves as Lewis acid as well as Lewis base?.
Saturday, February 8, 2020
What is Lewis acid character order of Boron halides, arrange in increasing order?
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Arrange the silicon halides into decreasing order of Lewis acids Character? SiF4, SiCl4, SiBr4, SiI4
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Tuesday, October 23, 2018
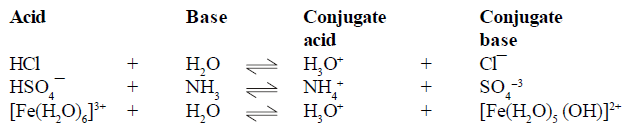
BRONSTED LOWERY ACID-BASE CONCEPT
For example
(1) conjugate pair is acid-base pair differing in single proton (H+)
(2) conjugate acid is written by adding H+ and conjugate is written by removing H+ .
(4) Equilibrium always moves from strong acid to weak acid and strong base to weak base.
MERITES OF BRONSTED CONCEPT:
(1) the role of solvent clearly defined.
(2) the acidic and basic character may be observed in non aqueous medium also .
(3) the acidic ,basic or Amphoteric nature of most of the substance may be defined.
(4) the acid having greater tendency to donate protons are stronger acid and base having greater tendency to accept protons are stronger base .
(5)In conjugate pair ,if one is strong then other must be weak .
The weak acid or base are normally determined by comparing the the stability of different acid or base
DEMERITES OF BRONSTED CONCEPT:
(1) Proton is a nuclear particle hence reaction should not explained in term of proton.
(2) the neutralized process becomes multiples step process.
(3) Most of the Amphoteric solvent become Amphoteric.
AMPHOTERIC SPECIES (Amphiprotic):
The species which have a tendency to donate proton as well as accept proton (H+) such species are known as Amphoteric species.
For example H2O,NH3 HS- ,HPO3- ,HC2OO4- , H2O4 etc
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES:
(1)The conjugate base of HCO3 is –
(A) H2CO3 (B) CO2 (C) H2O (D) CO3-
(2) The conjugate acid of HSO3- is -
(A) SO32- (B) SO42- (C) H2SO4 (D) H2SO3
(Ans: 1-D 2-D)
ARRHENIUS ACID-BASE CONCEPT
(1) acids convert blue litmus to red and methyl orange indicator to red .
(2) Sour in taste.
(3) It liberate hydrogen gas with active metals.
(4) Acids neutralised the effect of base
(5) acids increases the conduction of water.
CHARACTERS OF BASES:
(1) bases convert the red litmus to blue and methyl orange indicator to yellow.
(2) Phenylphthlene indicator (white) to pink.
(3) Bitter in taste and soapy in touch.
(4) Bases neutralised the effect of acid.
(5) They increases conductance of water.
ACID BASE CONCEPT:
(1) ARRHENIUS ACID-BASE CONCEPT
(2) BRONSTED LOWERY ACID-BASE CONCEPT
(3) LEWIS ACID-BASE CONCEPT
the substance which produces H+ in aqueous solution is consider as acid and the substance which give produces OH- in aqueous solution is consider as base
Arrhenius theory depend upon dissociation of water.
Type of Arrhenius acids:
Feature of Arrhenius theory:
Strength of acid or base:
(2) It could not explain formation of hydronium ions like H3O- , H5O2- , and H7O3- .
(3) the nature of aqueous solution of AlCl3, CuSO4 ,BF3, B(OH)3 etc are acidic and aqueous solution of NH3 ,NaCO3 ,RNH2 R2NH, R3N , C2H5N etc are basic in nature cannot be explain by Arrhenius Concept.
(4) there are many Amphoteric hydroxide Zn(OH)2 Al(OH)3 ,Pb(OH)2 , which cannot be explain by Arrhenius Concept.
(5) Arrhenius explain only when H+ is released it cannot explain when H+ is taken.