According to Bronsted theory the
species which donate protons (H+) in any medium is consider as acid and the
species which accept proton is consider as base.
Acid and base characters are realised in the presence of each other.
For example
For example
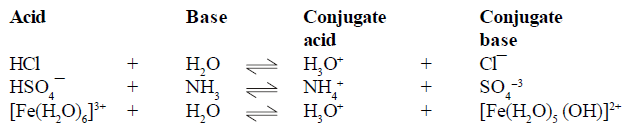
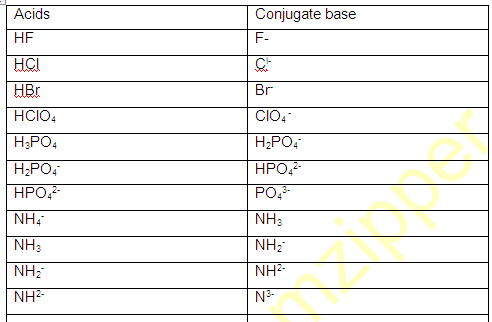
CONJUGATE
ACID-BASE PAIRS
(1) conjugate pair is acid-base pair differing in single proton (H+)
(2) conjugate acid is written by adding H+ and conjugate is written by removing H+ .
(3)
Strong acid has weak conjugate base and vice versa. Similarly strong base has
weak conjugate and vice versa.(1) conjugate pair is acid-base pair differing in single proton (H+)
(2) conjugate acid is written by adding H+ and conjugate is written by removing H+ .
(4) Equilibrium always moves from strong acid to weak acid and strong base to weak base.
MERITES OF BRONSTED CONCEPT:
(1) the role of solvent clearly defined.
(2) the acidic and basic character may be observed in non aqueous medium also .
(3) the acidic ,basic or Amphoteric nature of most of the substance may be defined.
(4) the acid having greater tendency to donate protons are stronger acid and base having greater tendency to accept protons are stronger base .
(5)In conjugate pair ,if one is strong then other must be weak .
The weak acid or base are normally determined by comparing the the stability of different acid or base
DEMERITES OF BRONSTED CONCEPT:
(1) Proton is a nuclear particle hence reaction should not explained in term of proton.
(2) the neutralized process becomes multiples step process.
(3) Most of the Amphoteric solvent become Amphoteric.
AMPHOTERIC SPECIES (Amphiprotic):
The species which have a tendency to donate proton as well as accept proton (H+) such species are known as Amphoteric species.
For example H2O,NH3 HS- ,HPO3- ,HC2OO4- , H2O4 etc
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES:
(1)The conjugate base of HCO3 is –
(A) H2CO3 (B) CO2 (C) H2O (D) CO3-
(2) The conjugate acid of HSO3- is -
(A) SO32- (B) SO42- (C) H2SO4 (D) H2SO3
(Ans: 1-D 2-D)
@@@



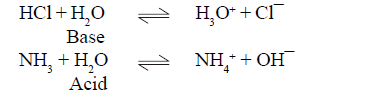

No comments:
Post a Comment