Important
Ores of Iron:
SN
|
Ores
|
Formula
|
1
|
Haematite (Red)
|
Fe2O3
|
2
|
Magnetite
|
Fe3O4
|
3
|
Siderite or Spathic
|
FeCO3
|
4
|
Iron Pyrite (fool’s
Gold)
|
FeS2
|
5
|
Goethite
|
FeO(OH)
|
6
|
Limonite
|
2Fe3O4.3H2O
|
Others Ores
|
||
7
|
Ilmenite (FeO+TiO2)
|
FeTiO3
|
8
|
Chromite (FeO+Cr2O3)
|
FeCr2O4
|
Extraction process of iron: Iron is extracted
from if oxide ores especially form the magnetite, Haematite, and Limonite ores.
The extraction involves the following process.
(1) Enrichment of concentration of
ores:
(A)Dressing or Benefaction of the ore: After mining, Iron ore is first broken into small pieces of 3 – 5 cm in size.
(B)Magnetic and Gravity Separation: Use due to the
presence of metal carbonate
(2) Conversion of ores into oxide
ores:
(A) Calcination: Heating ore in the absence of oxygen below melting
point moisture and CO2 are removed.
(B) Roasting: Heating of
ore in the presence of oxygen below melting point. During
roasting P, S, C, As, Sb etc. are oxidized to the respective oxides and removed.
(i) Fe3O4 is
decomposed to ferrous oxide (FeO) and ferric oxide (Fe2O3).
(ii) Ferrous oxide reacts with silica to
form ferrous silicate at high temperature.
(ii) The conversion of FeO into Fe2O3
will prevent the formation of FeSiO3 Thus mass of
the ore becomes porous causing the increase in the effective surface area.
(3) Smelting:
The
calcined ore is mixed with Limestone (Flux) and Coke (a reductant) and smelted in Blast
furnace.
Reaction in Blast furnace: A blast furnace is used for
smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such
as lead or copper. The blast
furnace is a huge, steel stack lined with refractory brick, where
iron ore, coke and limestone are dumped into the top, and pre heated air is
blown into the bottom.
(1) Zone
of combustion: (900 -1500 K): This is the higher temperature range found at
lower part of blast furnace
(2) Zone
of reduction: (500 – 800 K): This is lower temperature range found at upper
part of blast furnace.
(3) Zone
of slag formation: (1070-1270 K): Middle part of blast furnace:
Other impurities
like P4O10 and SiO2 and MnO2 also
reduced
(4) Zone of fusion: (1570 – 2170
K): lower part of furnace.
Molten iron is
heavier than molten slag. The two liquids are periodically tapped off and solidified into
blocks called pigs. And thus Iron obtained from blast furnace is
also called pig
Iron.
Type of Iron:
(1) Pig Iron: Composition:
SN
|
Impurities
|
%
|
1
|
Carbon (C)
|
3- 4.3
|
2
|
Silicon (Si)
|
1-2.0
|
3
|
Manganese (Mn)
|
0.5-2.0
|
4
|
Phosphorous (P)
|
0.05-2.0
|
5
|
Sulphure (S)
|
0.05-1.0
|
(2) White Cast Iron: When re molted pig iron is suddenly cooled,
white cast iron is results. In this form of cast iron carbon is found to be
combined form as cementite (Fe3C).
(3) Grey Cast Iron: However when re molted pig iron is slowly cooled,
Grey cast iron is results. In this form of cast iron carbon is found to be
combined form of Graphite.
(4) Wrought
iron:
This is done by
heating cast iron with haematite (Fe2O3) which oxidises C
to CO, S to SO2 Si to SiO2, P, P4O10
and Mn to MnO . Where CO and SO2 escapes, manganese oxide (MnO) and
Silica (SiO2) combine to form slag.
Similarly
phosphorus pentoxide combines with haematite to form ferric phosphate slag.
Manufacturing
Process:
Casts
iron takes in Puddling
furnace and melted by hot blast of air. The chemical reactions which
occur are:-
On
removing impurities, the melting point rises and it becomes a semi solid mass.
The metal is taken out of the furnace in the form of balls which are then beaten under
hammer to separate out the slag. The product thus formed is thus called wrought iron.






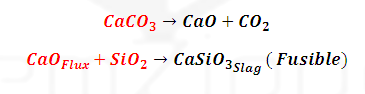

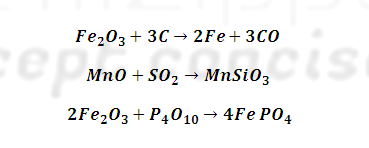

No comments:
Post a Comment