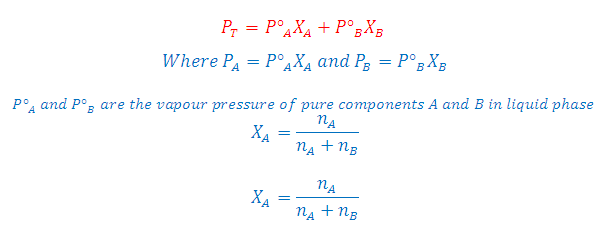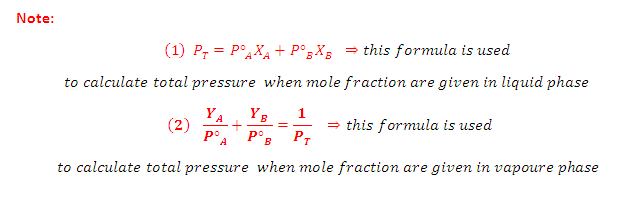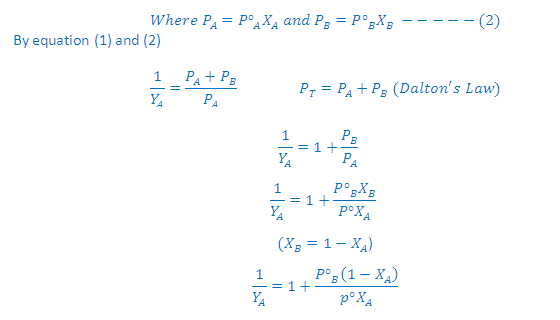Search This Blog
Sunday, May 24, 2020
Which of the following pair of solution (aq.) contain isotonic solution at same temperature? (Assume 100 % ionisation of electrolytes) (1) 0.1 M NaCI and 0.2 M CaCI2(2) 0.1 M NaCI and 0.3 M AICI3 (3) 0.3 M NaCI and 0.1 M AICI3 (4) 0.3 M NaCI and 0.2 CaCI2
Freezing point of pure liquid A is T K. If some amount of non-electrolyte non-volatile impurity is added in A, an ideal solution is formed. On cooling at 200 K, only 30% (by mass) liquid A is present and at 201 K, 60 % (by mass) liquid A is present. The value of T is .
Liquid A and B form ideal solution at temperature T. Mole fraction of A in liquid and vapour phase are 0.4 and 4/13 respectively, when total pressure is 130 torr. The vapour pressure (in torr) of A and B in pure state at temperature T are respectively.
We know that partial pressure of components of a binary solution containing A and B component.
(1) In liquid state:
P_A= P°_A X_A and P_B= P°_B X_B
(2) In Vapour phase:
P_A= P_T Y_A and P_B= P_T Y_B
Where X_A and X_B is mole fraction in liquid state while Y_A and Y_B is mole fraction in vapour phase
What is the relation between Raoult' law and Dalton's ?
According to Raoult's Law: The partial pressure of any volatile component of a solution at any temperature is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by the mole fraction of that component in the solution.
Where XA and XB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in liquid phase respectively
According to Dalton's Law:
The vapour behaves like an ideal gas, then according to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PTis given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
PA = PT YA and PB =PT YB
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
Combination of Raoult's and Dalton's Law:
(3) Thus, in case of ideal solution the vapour phase is phase is richer with more volatile component i.e., the one having relatively greater vapour pressure
Graph Between 1/YA Vs 1/XA:
According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PT is given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
According to Raoult's law:
On rearrangement of this equation we get a straight line equation:
Illustrative Examples:
Saturday, May 23, 2020
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)