The square planar arrangement of
ligands may be considered to be one derived from the octahedral field by removing
two trans-ligands located along the Z-axis. In the process, the eg and t2g
sets of orbitals is lifted i.e., these orbitals will no longer be degenerate.
The four ligands in square planar
arrangement around the central metal ion are shown in Fig. As the ligands approach
through the axes, they would have greatest influence on dx2-y2 orbital, so the energy of this orbital,
will be raised most. The dxy
orbital, lying in the same plane, but between the ligands will also have a greater
energy though the effect will be less than that on the dx2-y2 orbitals. On the other hand, due to absence
of ligands along Z-axis, the z2d
orbital becomes stable and has energy lower than that of dxy orbital.
Similarly dyz and dxz
become more stable. The energy level diagram may be represented as Fig. along
with tetrahedral and octahedral fields.
The value of del.sp
has been found larger than del.oct because of the reason that dxz and dyz orbitals interact with only two ligands in the
square planar complexes, while in octahedral complexes the interaction takes
place only with four ligands. del.sp has been found equal to 1.3 del.oct
FACTORS
FAVOURING SQUARE PLANAR:
(1) Metals (atom/ion) with
configuration 4d8 or 5d8 always form square planar
complexes irrespective of natureof the liqand. Such metal atom or ions are as
[PtCl4
]1-although Cl1- are W.L.yet is is square planar complex
(2) But with the metal atom or the ion
with 3d8 configuration, for example Ni(II)) complex will be square
planar only with the strong field ligands. (tetrahedral with weak ligand).
Others Examples:


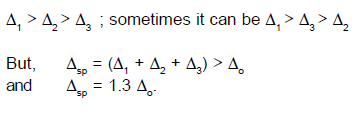
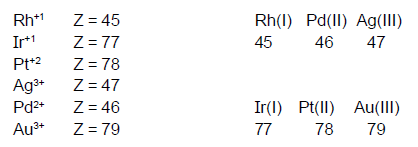

No comments:
Post a Comment