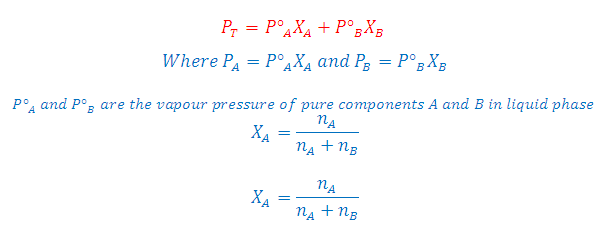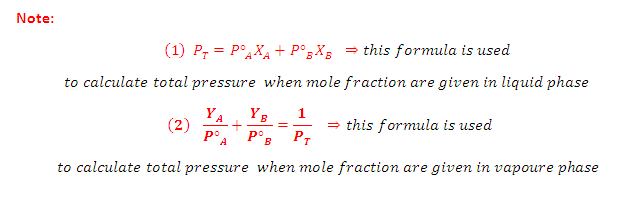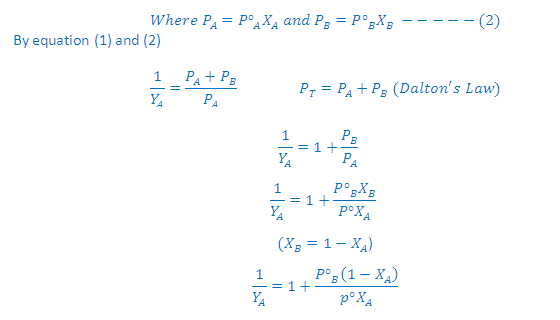Search This Blog
Thursday, November 25, 2021
A metal slowly forms an oxide film which completely protects the metal when the film thickness is 3.956 thousands of an inch. If the film thickness is 1.281 thousands. in 6 weeks, how much longer will it be before it is 2.481 thou? The rate of film formation follows first order kinetics.
Tuesday, November 23, 2021
Class Claperon equation:
Vapour pressure is directly proportional to the Temperature so that on increasing temperature the rate of evaporation increases and rate of condensation decreases and hence vapour pressure increases.
The dependence of vapour pressure and temperature is given by CLASIUS CLAPERON equation.
Related topics:
Thursday, November 18, 2021
How many of the elements exist as gases at 25°c?
H,N,O, flourine (F), Chlorine (Cl),He, Neone (Ne) , Argone (Ar) kriptane (Kr) , Xenone (Xe) these are the elements found in gaseous state at 25℃ present in periodic table.(2) What are the Amphoteric metals ? gives Examples.
(4) What is Mendeleev's periodic table ? give important features and draw back of Mendeleev's table.
(5) What is atomic density ? give the periodicity of atomic density in periods and groups.
(6) What is atomic volume ? and what is periodicity of atomic volume in groups and periods ?
(7) Why there are 2, 8 and 8 elements in first, second and third periodic of periods table respectively ? Explain.
(8) In alkali metal group which is the strongest reducing agent in aqueous solution and why?
(9) The electron affinity of sulphur is greater than oxygen. Why?
Related Questions:
(1) Total numbers of elements which are liquid at normal temperature is ?
(2) What are the Amphoteric metals ? gives Examples.
(3) Name of total metalloids present in periodic table ?
(4) What is Mendeleev's periodic table ? give important features and draw back of Mendeleev's table.
(5) What is atomic density ? give the periodicity of atomic density in periods and groups.
(6) What is atomic volume ? and what is periodicity of atomic volume in groups and periods ?
(7) Why there are 2, 8 and 8 elements in first, second and third periodic of periods table respectively ? Explain.
(8) In alkali metal group which is the strongest reducing agent in aqueous solution and why?
(9) The electron affinity of sulphur is greater than oxygen. Why?
(10) The first ionization energy of carbon atom is greater than that of boron atom, whereas reverse is true for the second ionization energy. Explain.
Monday, November 15, 2021
Liquid A and B forms an ideal solution and initial vapour pressure of A and B are P°A= 0.4 atm and P°A= 0.6 atm respectively. In a cylinder piston arrangement, 2 mole vapour of A and 3 mole vapour of B is collected at 0.42 atm.
(1) predict wheather the vapour will condense or not ?
(2) If the vapours are compared slowly and isothermally at what pressure F drop of liquid will form?
(3) If initial volume of vapour was 10 litre , at what volume first drop of liquid is form?
(4) What is the composition of first drop of liquid formed?
(5) If vapour pressure are further compressed. At what pressure almost complete condensation of vapour will occure?
(6) Determine the composition of last traces of vapours remains?
(7) What is the composition of system at 0.55 atm pressure?
(8) Determine the composition of liquid and vapour formed at 0.51 atm also calculate the moles of liquid of A and B in liquid and vapour formed ?
(9) At what pressure half of the total amount of vapour will condense?
Related Questions;
Sunday, November 14, 2021
Vapour pressure of a solution containing 6 gm of non volatile solute in 180 gm of water is 20 torr/mmHg. If 1 mole of water is further added in to the V.P. increases by 0.02 torr. calculate the V.P. of pure water and molecular wt of the non volatile solute.
What is relation between relative lowering of vapour pressure and molality of solution?
ILLUSTRATION
Related Questions;
Saturday, November 13, 2021
200 ml of 0.2M urea solution is mixed with 200 ml of glucose solution at 300 K. Calculate osmotic pressure of resulting solution.
Friday, November 12, 2021
How to determine total vapour pressure of solution in liquid phase as well as gas phase ?
According to Raoult's Law: The partial pressure of any volatile component of a solution at any temperature is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by the mole fraction of that component in the solution.
Where XA and XB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in liquid phase respectively
According to Dalton's Law:
The vapour behaves like an ideal gas, then according to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PTis given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
PA = PT YA and PB =PT YB
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
Combination of Raoult's and Dalton's Law:
(3) Thus, in case of ideal solution the vapour phase is phase is richer with more volatile component i.e., the one having relatively greater vapour pressure
Graph Between 1/YA Vs 1/XA:
According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PT is given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
According to Raoult's law:
On rearrangement of this equation we get a straight line equation:
Illustrative Examples:
Wednesday, November 10, 2021
When a solution containing w of urea in 1kg of water is cooled to 272K, 200g of ice is separated. If for water is 1.86Kkgmol−1,w is:
What is Azeotropic mixture or solution?
A solution which boils like a pure liquid and has same composition in liquid as well as vapour phase is called Azeotropic solution or mixture.
Features of Azeotropic mixture:
# For Azeotropic solution XA =YA
# An ideal solution can not form Azeotropic mixture.
# only non ideal solution form Azeotropic mixture.
# composition of Azeotrope alter on changing external pressure.
# Azeotropic solution can't separated by fractional distillation.
Type of Azeotropic solution or mixture:
(1) Minimum boiling Azeotropic solution.
It is formed by solution which show positive (+) deviation from ideal behaviour. Such solution has boiling point smaller than boiling point of both of components liquids.
For example, mixture of 95% ethanol by weight and 4% of water.
Water boils at 373 K, and ethanol boils at about 351.5K, while azeotropes mixture of both boil at around 351.15 K, suggesting a boiling point lower than its constituents.
(2) Maximum boiling Azeotropic solution.
It is formed by solution which show negative (-) deviation from ideal behaviour. Such solution has boiling point larger than boiling point of both of components liquids.
For example, mixture of approximately 20% by weight hydrochloric acid and 79 % of water.
Water boils at 373 K and hydrochloric acid boil at about 188 K, while azeotropes of both boil at around 383 K which is a boiling point greater than its constituents.
Related Questions;
(2) Acetic acid dimerised to an extent of 30% in benzene . The observed molecular mass (in gm) is...
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)