According to Raoult's Law: The partial pressure of any volatile component of a solution at any temperature is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by the mole fraction of that component in the solution.
Where XA and XB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in liquid phase respectively
According to Dalton's Law:
The vapour behaves like an ideal gas, then according to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PTis given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
PA = PT YA and PB =PT YB
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
Combination of Raoult's and Dalton's Law:
(3) Thus, in case of ideal solution the vapour phase is phase is richer with more volatile component i.e., the one having relatively greater vapour pressure

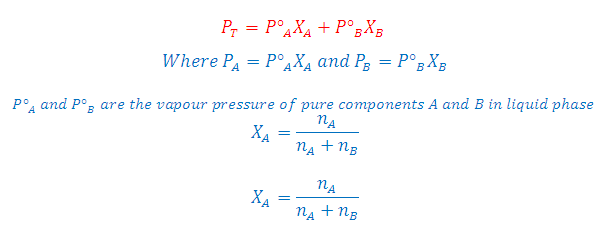

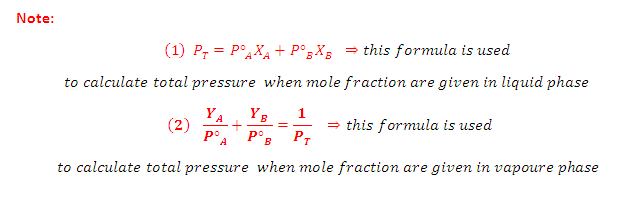
No comments:
Post a Comment