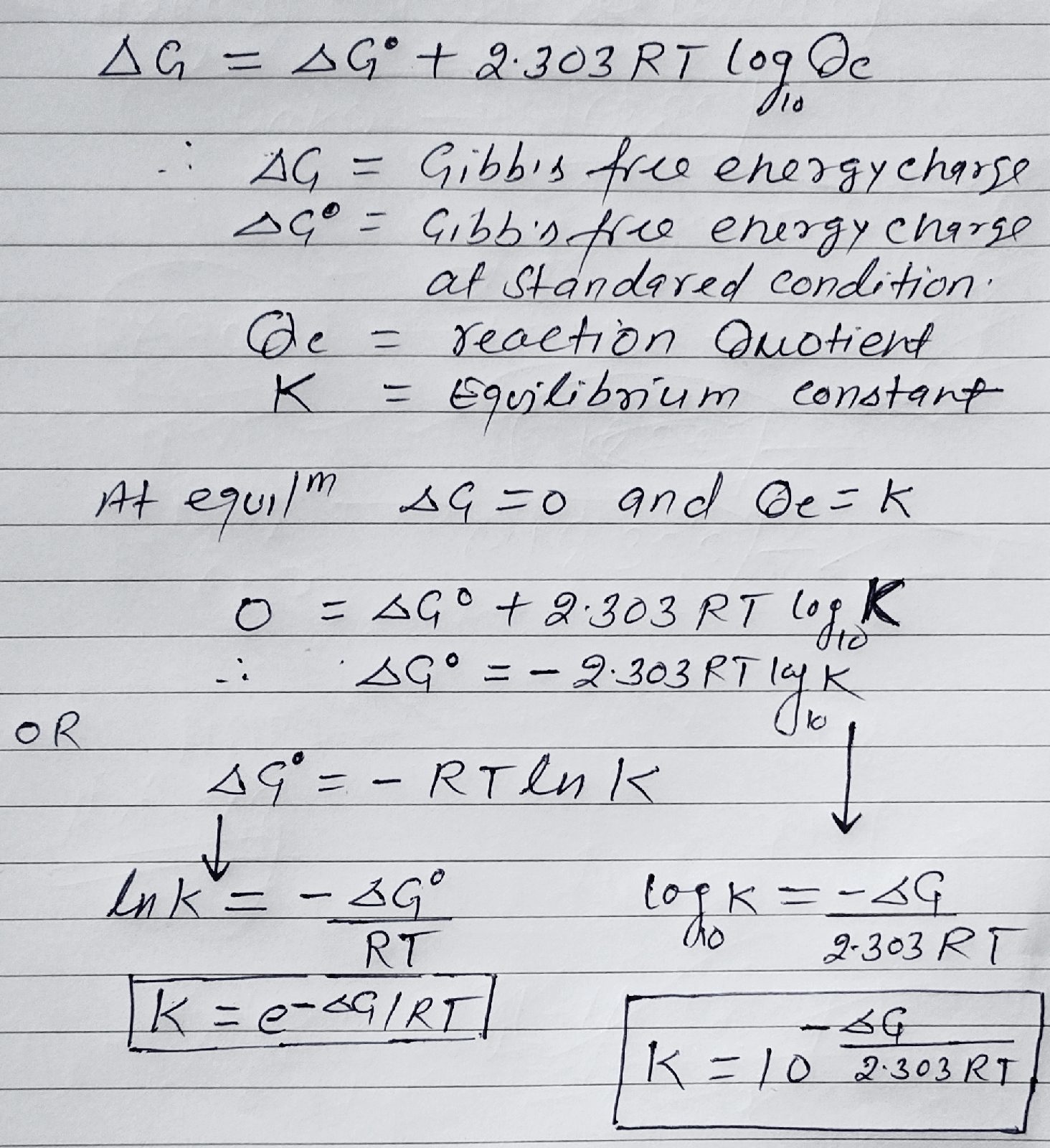Search This Blog
Friday, September 29, 2023
4 mole of an ideal gas having γ = 1.67 are mixed with 2 mole of another ideal gas having γ = 1.4. Find the equivalent value of γ for the mixture.
Answer key: γ= 1.54
Sunday, September 17, 2023
Titration of Weak acid Vs Strong base:
(II): Titration of Weak acid Vs Strong base:
Titration of a weak acid
by strong base is a bit more complex than both acid and base are strong this is
because we have consideration the equilibrium involving the weak acid and its
conjugate base.
Titration Table and curve:
|
S.N |
Acid
(0.1M) |
Base (0.1M ) |
pH |
Nature |
Case |
|
1 |
|
0 ml |
2.85 |
WA |
pH=1/2(Pka –logC) |
|
2 |
Volume |
5 ml |
4.22 |
ABS |
pH=(Pka +log [S]/[A] |
|
3 |
Taken |
10 ml |
4.7 |
ABS |
pH=Pka Best Buffer |
|
4 |
20.0 ml |
15 ml |
5.17 |
ABS |
pH=(Pka +log [S]/[A] |
|
5 |
Ka for |
19 ml |
5.98 |
ABS |
pH=(Pka +log [S]/[A] |
|
**6 |
CH3COOH |
20 ml |
8.7 |
SH |
pH=7+1/2(Pka+logC) |
|
7 |
2* 10^-10 |
21 ml |
11.39 |
SB |
NbVb - NaVa=NrVr |
|
8 |
|
25 ml |
12.04 |
SB |
[OH-]= Nr |
|
9 |
|
30 ml |
12.3 |
SB |
Strong base |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
Remains present |
In titration of any weak acid with strong base, The pH at equivalent point will be greater than “7”
Sunday, September 10, 2023
ΔG^ o at 25^°C for the reaction 1/2N2(g) + 3/2H2(g) ⇋ 2NH3(g) is -11.392 kj mole^-1. Hence thermodynamics equilibrium constant is : he equilibrium constant for reaction is 10. (Use R=8.3 JK ^−1 mol ^−1)
Answer key : 10^2
The dissociation equilibrium of a gas AB2 can be represented as : 2AB2(g) ⇋ 2AB(g) + B2(g) The degree of dissociation is "x" and is small compared to 1. The expression relating the degree of dissociation (x) with equilibrium constant Kp and total pressure P is.
Friday, September 8, 2023
Relation between Kp and Kc:
When concentration are expressed in terms of mole fractions.
We know that partial pressure (P) = Mole fraction × Total pressure (Pt)
Thursday, September 7, 2023
Tuesday, September 5, 2023
A certain Zero order reaction has rate constant K is 0.025 MS^-1 for disappearance of A . What will be the concentration of A after 15 sec if initial concentration is A is 0.5M.
(A) 2.5 M (B) 0.5 M (C) 1.5 M (D) 0.125 M
The rate constant for zero order reaction is 2× 10^-2 Mole L^-1 sec-1. If the concentration of reactant after 25 sec is 0.5M ,the initial concentration must have been ?
(A) 1M (B) 2M (C) 1.5M (D) 2.5M
Consider a general reaction A--->B follow zero order kinetics.if concentration of A is reduces from 0.1 M to 0.05 M in 10 second then calculate time taken when concentration reduce to 0.025 M.
(A) 2.5 sec (B) 2 sec (C) 5 sec (D) 10 sec
Sunday, September 3, 2023
Equilibrium constant for the reaction given below is 2.0 × 10^-7 at 300 K. calculate standard Gibb's free energy change for the reaction PCl5 (g) --=--PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) also calculate standard entropy change if ∆H° = 28.40 Kj mole-1.
Saturday, September 2, 2023
Gibb's free energy (∆G) and Equilibrium constant (Kc):
The part f energy which is converted into usefull work called Gibb's free energy or Gibb's function.
Energy (H) = Useful work (G) + Non useful (TS)
We van not calculate absolute value of 'G' so we calculate change in Gibb's free energy.
∆G = ∆H -∆TS
∆G = ∆H - (∆TS + T∆S). ......(1)
Standard Gibb's energy (∆G°) change at standard condition is 1 bar and 298 K
∆G° = ∆H° -∆TS° .......(2)
Relation between ∆G° and Equilibrium constant (K):
Topic:
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:
Factor's Affecting Equilibrium Constant
(1) Le-Chetelier'e principle
(i) Effect of change in temperature
(ii) Effect of change in concentration
(iii) Effect of change of volume of container at equilibrium
(iv) Effect of change in pressure
(v) Effect of Catalyst at equilibrium
(vi) Effect of Addition of Inert gas
(a) At constant volume
(b) At constant pressure
[End of Chapter = ∆∆∆]
Topic:
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:
Application of Equilibrium Constant (K):
(1) Predicting extent of reactions
(2) Predicting of stability of reactants and products
(3) Predicting direction of reactions at any instant of reaction (Qc)
(4) Predicting concentration of reactants and products at equilibrium.
(5) Degree of dissociation and Kp and Kc in term of DOD.
(6) Degree of dissociation and Vapour density.
Topic:
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM:
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)