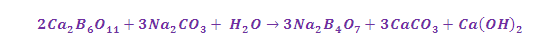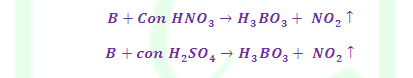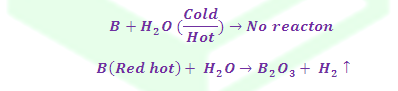Boron is metalloids of 13th
group and it does not occur in Free State. The major ores of boron are a small
number of borate (boron oxide) minerals, including
PREPARATION OF BORON:
(1) From Borax: Boron may be obtained by
treating borax with hot concentrated HCl, or H2SO4, igniting the boric acid H3BO3 to give the oxide B2O3 and finally reduced with
Na, K, Al, Mg.
Step-(1) conversion of borax into boron oxide:
Step-(2) conversion of Boron oxide into boron:
(2) From Colemanite:
Physical properties:
(1) It is a non-metal. Boron occurs in two different
allotropic forms Amorphous and Crystalline
(2) Amorphous boron has not been obtained in the pure
state.
(3) Crystalline boron is a black powder, extremely hard
with a metallic appearance but with very low electrical conductivity.
Chemical properties:
(1) Reaction with non oxy acids:
(2) Reaction with Oxy acids:
(3) Reaction with Oxy water:
(4) Reaction with Base:
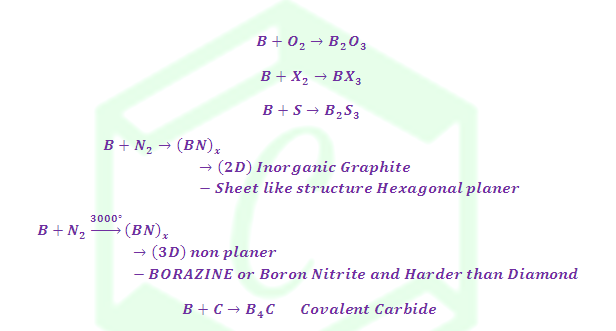
(5) Reaction with Metals:
(6) Reaction with Non-metals
(7)
Reaction with Ammonia:
Structure of Borazine: