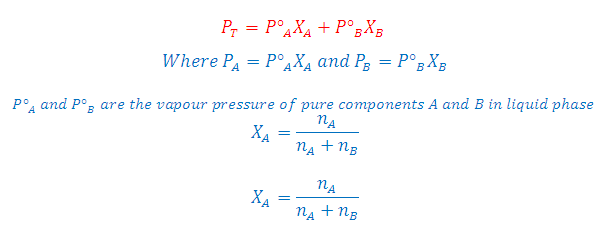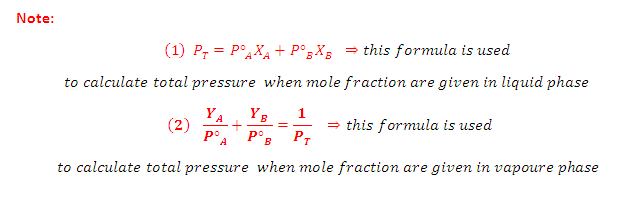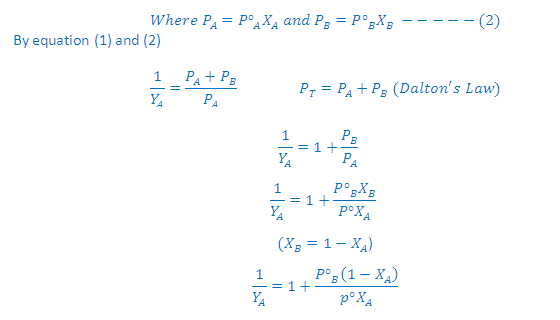Search This Blog
Saturday, November 13, 2021
Friday, November 12, 2021
How to determine total vapour pressure of solution in liquid phase as well as gas phase ?
According to Raoult's Law: The partial pressure of any volatile component of a solution at any temperature is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure component multiplied by the mole fraction of that component in the solution.
Where XA and XB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in liquid phase respectively
According to Dalton's Law:
The vapour behaves like an ideal gas, then according to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PTis given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
PA = PT YA and PB =PT YB
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
Combination of Raoult's and Dalton's Law:
(3) Thus, in case of ideal solution the vapour phase is phase is richer with more volatile component i.e., the one having relatively greater vapour pressure
Graph Between 1/YA Vs 1/XA:
According to Dalton's law of partial pressures, the total pressure PT is given by:
Partial pressure of the gas = Total pressure x Mole fraction
Where YA and YB is the mole fraction of the component A and B in gas phase respectively
According to Raoult's law:
On rearrangement of this equation we get a straight line equation:
Illustrative Examples:
Wednesday, November 10, 2021
When a solution containing w of urea in 1kg of water is cooled to 272K, 200g of ice is separated. If for water is 1.86Kkgmol−1,w is:
What is Azeotropic mixture or solution?
A solution which boils like a pure liquid and has same composition in liquid as well as vapour phase is called Azeotropic solution or mixture.
Features of Azeotropic mixture:
# For Azeotropic solution XA =YA
# An ideal solution can not form Azeotropic mixture.
# only non ideal solution form Azeotropic mixture.
# composition of Azeotrope alter on changing external pressure.
# Azeotropic solution can't separated by fractional distillation.
Type of Azeotropic solution or mixture:
(1) Minimum boiling Azeotropic solution.
It is formed by solution which show positive (+) deviation from ideal behaviour. Such solution has boiling point smaller than boiling point of both of components liquids.
For example, mixture of 95% ethanol by weight and 4% of water.
Water boils at 373 K, and ethanol boils at about 351.5K, while azeotropes mixture of both boil at around 351.15 K, suggesting a boiling point lower than its constituents.
(2) Maximum boiling Azeotropic solution.
It is formed by solution which show negative (-) deviation from ideal behaviour. Such solution has boiling point larger than boiling point of both of components liquids.
For example, mixture of approximately 20% by weight hydrochloric acid and 79 % of water.
Water boils at 373 K and hydrochloric acid boil at about 188 K, while azeotropes of both boil at around 383 K which is a boiling point greater than its constituents.
Related Questions;
(2) Acetic acid dimerised to an extent of 30% in benzene . The observed molecular mass (in gm) is...
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)