The
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) was originally proposed for explaining the optical
properties of crystalline solids. It was applied to the study of coordination
compounds in the 1950s. CFT assumes the ligands to be point
charges and the interaction between them and the electrons of the central metal
to be electrostatic in nature. The five d-orbitals in an isolated
gaseous metal atom/ion have same energy, i.e., they are degenerate. This degeneracy is maintained if a
spherically symmetrical field of negative charges surrounds the metal atom/ion.
However, when this negative field is due to ligands (either anions or the
negative ends of dipolar molecules like NH3 and H2O) in a
complex, it becomes asymmetrical and the
degeneracy of the d-orbitals is lifted. It results in splitting of the
d-orbital energies. The pattern of splitting depends upon the nature of the crystal
field. We will first consider:
(1) CRYSTAL FIELD SPLITTING IN OCTAHEDRALCOMPLEXES:
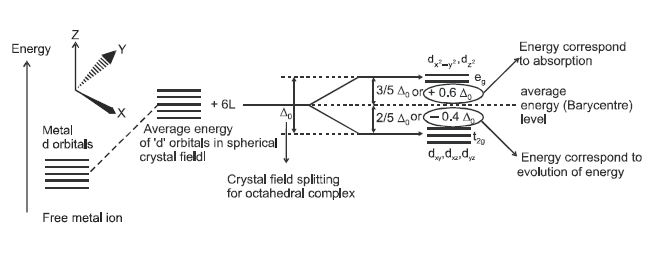
For
convenience, let us assume that the six ligands are positioned symmetrically
along the Cartesian axes, with the metal atom at the origin. As the ligands
approach, first there is an increase in the energy of d orbitals to that of the
free ion just as would be the case in a spherical filed. Next, the orbitals
lying along the axes (dz2and dx2-y2 d)
get repelled more strongly than dxy, dyz and dxz orbitals,
which have lobes directed between the axes. The dxy , dyz , dxz
orbitals are lowered in energy relative to the average energy in the spherical
crystal filed.
Thus, the degenerate set of d orbitals get split into two sets: the lower
energy orbitals set, t2g and the higher energy, eg set.
The energy separation is denoted by del.oct (the subscript o is for octahedral.
CRYSATAL FIELD STABLISATION ENERGY:
(3) CRYSTAL FIELD SPLITTING IN SQUARE PLANER COMPLEXES:

No comments:
Post a Comment