The mechanisms that accounts for the
experimental observations involves formation of a benzene intermediate which has
two equivalent carbon atoms to which amino group can be attached. Benzyne has
an extra (Pi) bond between two adjacent carbon atoms of benzene and can be
formed as
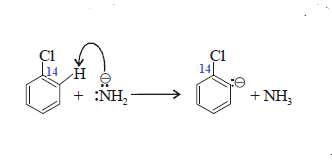
Step-(1): Strong base NH2- removes a proton
from the position ortho to halogen:
Step-(2): Anion formed in step (1) eliminates the halide
ion, thereby forming Benzyne:
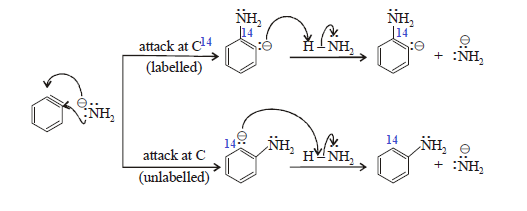
The incoming nucleophile can attack
either of the carbons of the “triple bond” of benzyne. Protonation of the
resulting anion form the substitution product. The overall reaction is an
elimination-addition reaction; benzyne is formed in an elimination reaction and
immediately undergoes an addition reaction.
Substitution at the carbon (C-14) that
was attached to the leaving group is called direct substitution product (DSP).
Substitution at the adjacent labeled carbon (C-14) of is called cine
substitution product (CSP).




No comments:
Post a Comment