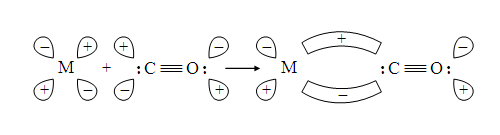Compounds that contain at least one
carbon-metal bond are called organometallic compounds. Zeisse, in 1830,
prepared the first organometallic compound by the action of ethylene on a
solution of potassium chloroplatinate (II). In the last four decades, enormous
work has been done in this field any many fascinating compounds have been
synthesised and investigated. Grignard reagent, R-Mg-X is a familiar example of
organometallic compounds where R is an alkyl group. Diethyl zinc [Zn(C2H5)2]
, lead tetraethyl [Pb(C2H5)4] , ferrocene
[Fe(C5H5)2]
dibenzene chromium [CrC6H6)2] metal
carbonyls are other examples of organometallic compounds. The compounds of
metalloids such as germanium and antimony and non-metallic elements such as
boron and silicon are also included under this classification.
Organometallic compounds may be
classified in three classes :