The carbocaton contaning hetero
atoms adjacent to positive carbon of cation such as
oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur etc which are more electronegative than carbon,
you might expect that they would by definition be electron withdrawing groups
that destabilize carbocations.
But there
is opposite effect, if the oxygen, nitrogen or sulphur atom is present at
adjacent to carbocation, the overall effect is carbocation stabilization.
This
is due to the fact that although these heteroatoms are electron withdrawing groups by induction, they are electron donating groups by resonance, and it is
this resonance effect which is more powerful.
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE(1): Give the correct Stability of given carbocation .
SOLUTION: Sulphur containing carbocation is more stable because lone pair of sulphur atom show more resonating effect due to least electronegativity as compared to nitrogen as well as oxygen atom similarly nitrogen show more resonance than oxygen atom
Conceptual Facts:
(1) If number of conjugation increases stability of carbocation increases ...
(2) We known that on increasing conjugation stability increases. their is exception in option (A) their is three nitrogen may involving in resonance but actually not,
Because positive carbon does not involved in resonance due to bridge head carbon. we known according to
Bredt,s rule bridge carbon cannot for duble bond.
Hence correct stability order is (B) > (C) >> (A):
(3) Similarly
Hence correct stability order is (B) > (C) >> (A):
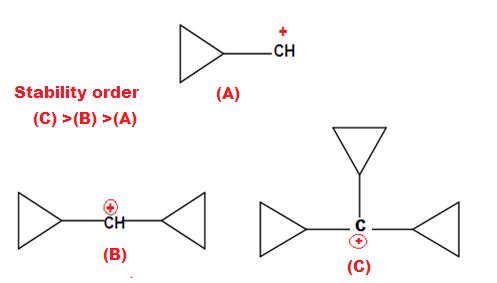
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE(3): Give the correct Stability of given carbocation.
SOLUTION: (1): (C) > (B) > (A) and (2): (C) > (B) > (A)
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE(4): Give the correct Stability of given carbocation.
SOLUTION: (1): (D) > (B) > (C) > (A) and (2): (D) > (B) > (C) > (A)
Other important examples:
IIT UPDATE:
QUESTION(1)
SOLUTION: (D)