AZT,
the abbreviation for azidodeoxythymidine, is a drug that treats human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immune defi ciency
syndrome (AIDS). Also known by its generic name zidovudine,
AZT represents a chemical success to a different challenge:
Search This Blog
Wednesday, January 1, 2020
Fluoxetine: Antidepressant:
Fluoxetine is a oral capsule its the generic name for
the antidepressant Prozac and Prozac Weekly. Prozac was
designed and synthesized by chemists in the laboratory, and is now produced on
a large scale in chemical factories. In
some cases, they may not be available in every strength or form as brand-name
drugs. . For the treatment of depressive episodes related to bipolar I disorder
and treatment-resistant depression, this drug must be used with olanzapine
Topic:
Organic Molecules-Medicine:
Amoxicillin:Antibiotics:
Amoxicillin is one of the most widely used antibiotics in
the penicillin family. The discovery and synthesis of such antibiotics in the
twentieth century have made routine the treatment of infections that were
formerly fatal. You were likely given some amoxicillin to treat an ear infection
when you were a child.
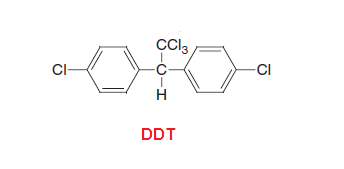
DDT(dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane):
Topic:
Organic Molecules-Medicine:
DDT- DichloroDiphenylTrichloroethane:
DDT,
the abbreviation for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, is a colorless,
tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochlorine. DDT use as pesticide and also called “miraculous”
by Winston Churchill because of the many lives it saved by killing disease carrying
mosquitoes.
DDT
was first synthesized in 1874 by the Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler.
DDT's insecticidal action was discovered by the Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller in 1939. DDT was used in the second half
of World War II to control malaria and typhus among civilians and troops. DDT
use is now banned in the United States and many developed countries because it
is a nonspecific insecticide that persists in the environment
Topic:
Organic Molecules-Medicine:
Reactivity order of Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene towards Electrophilic substitution :
Pyrrole, furan and thiophene undergo electrophilic substitution
reactions like nitration, sulphonation, halogenation etc. characteristic of
aromatic rings. That carbons in 5-membered heterocyclic rings have higher
electron density compared to benzene and hence undergo electrophilic
substitution more readily than benzene.The electrophilic substitution takes
place preferentially at 2-position (C-2).
The attack of an electrophile on pyrrole, for
example, will lead to formation of 2- and 3-substitution products by way of
carbocations (1) and (2) respectively.The substitution occurs preferably at C-2 position
because the intermediate obtained by attack at this position is more stable
than the intermediate obtained by attack at C-3. The positive charge in
intermediate (1) is more delocalized than
intermediate (2) and hence is more stable
and preferred intermediate.
The electrophilic
substitution at C-2 in furan and thiophene can also be accounted in the same
manner. Furan is not as reactive as pyrrole in electrophilic substitution
reactions because the oxygen in furan is more electronegative than nitrogen in
pyrrole and therefore does not enhance the electron density of carbons as much
as pyrrole. Thiophene is less reactive than furan towards electrophilic
substitution because the p-electrons of sulphur are in 3p orbital which
overlaps less effectively than the 2p orbital of nitrogen or oxygen with 2p
orbitals of carbon. The relative reactivities towards electrophilic
substitution follows the order:
SIR effect:
Dancing Resonance:
Inversion of Amines:
Topic:
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)