Search This Blog
Tuesday, February 11, 2020
What are "pyro" oxy acids?
What are "Ortho" or "Meta" oxyacids?
[The tendency of polymerisation is observed as SiO4 4- > PO4 3- > SO4 2- > ClO4 -]
Related Questions:
What are "pyro" oxy acids?Why SF6 behave inert towards hydrolysis?
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Arrange in increasing order of extent of hydrolysis [ CCI4, MgCI2, AICI3, PCl5, SiCI4].
Although Sulphur contain vacant d-orbital but SF6 does not under go hydrolysis. Why ?
CCl4 can not be hydrolysed but SiCl4 can be. Why?
Silianol (SiH3OH) is more acidic than methanol (CH3OH) why?
Saturday, February 8, 2020
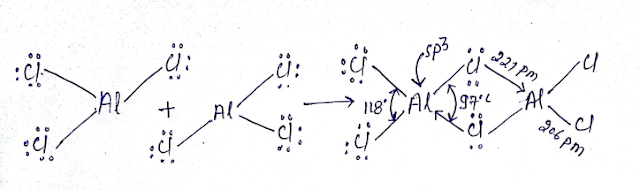
Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
Aluminium forms covalent
compound with chloride because lonisation enthalpy (∆iH= +5137 kJ/mole) of Aluminium is very high due to small size
and chlorine is unable to convert Al into Al+3 ions.
However, when
anhydrous AlCl3 (which is covalent in character) is
dissolved in water, it undergoes hydration as follow:
Al2CI6 + H2O --> 2[Al(H2O)6]+3 + (∆H)
Hydration of anhydrous aIuminium chloride is highly exothermic in nature. The hydration enthalpy is more than ionisation enthalpy of aluminium.This hydration enthalpy removes all the three valence electrons of the aluminium leading to the formation of Al3+ more easly.This AI3+ is hydrated with water and form a complex ion. Thus in water Al exist as [Al(H2O)6]+3 . The three electrons of aluminum is accepted by CI of AlCl3. Thus hydrated AlCl3 represented [Al(H2O)6]Cl3 and it is ionic in nature.
Related Questions:
(1) Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
(2) Why Ga has small size than Al exceptionally
(3) Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
(4) What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
(5) What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
(6) Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
(7) Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
(8) Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
(9) Why B-F do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
(10) Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
(11) Why Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
(12) Four-center two-electron bond (4C-2e Bond): Structure of AlCl3:
(13) What is the molecular formula of Borax ?
(14) What is the difference between the structure of AlCl3 and diborane?
What is Lewis acid character order of Boron halides, arrange in increasing order?
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Friday, February 7, 2020
The tendency of polymerisation is observed as SiO4 4- > PO4 3- > SO4 2- > ClO4 - Explain.
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Related Questions:
What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Arrange in increasing order of extent of hydrolysis [ CCI4, MgCI2, AICI3, PCl5, SiCI4].
Although Sulphur contain vacant d-orbital but SF6 does not under go hydrolysis. Why ?
(1) What are the SESQUI OXIDES ? give the examples.
Wednesday, December 26, 2018
BRIDGE BONDING-MULTI-CENTERED BOND:
Bond angle between bridge bonds is less than bond angle between terminal bonds.
Bond energy of 3C-2e bond is found to be higher than 2C-2e bond for same substitute. It may also be true for 4C-4e bond.
During formation of bridge bond empty atomic orbitals of central atom participate in hybridization.
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES (1):
(1) 3C-2e Bond Or Banana Bond
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (6): Which of the following molecule is/are dimerized by co-ordination bond?
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (8): Which one of the following statements is not true regarding diborane?
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (9): The structure of diborane (B2H6) contains
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (10): The molecular shapes of diborane is shown:
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE (12):