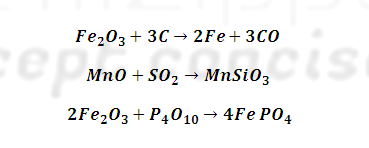Search This Blog
Monday, June 29, 2020
What is the percentage of Cl2 in bleach?
Is chlorine a bleaching agent?
Is chlorine a permanent bleaching agent?
Sunday, June 28, 2020
Saturday, June 27, 2020
What are the structure of CO2 , NO2+ , OCN- , SCN- ?
Why does CO form a coordinate bond?
How can draw the Lewis Structure of CO?
The electronic configuration of carbon and oxygen atoms as
C6 =1s2 2s2 2p2
O8 =1s2 2s2 2p4
This information can be used to determine the Lewis Dot Structure of Carbon monoxide (CO):
Step 1: calculate total valence electrons for carbon and oxygen atoms.
C = 4
O = 6
Total electrons in CO molecule =10
Step 2: Find octet electrons for each atom , carbon and oxygen
C: 8
O: 8
Total octet electrons =16
Step 3: Find the bonding electrons Subtract total valence electron from total octet electrons
16-10=6 electron (3 bond pair)
Step 4: Find number of bonds between carbon and oxygen atoms by dividing the number of bonding electrons by 2
6-electrons/2 = 3 bonds
Step 5: The rest are non bonding pairs. Subtract bonding electrons from valence electrons .
The Lewis structure of CO is identical with that for HC:::CH except that the C-H bond pair replace by lone pairs.
"CO is also isoctronic with CN-"
How can describe the bonding in PF5 using hybrid orbital?
What is Arrhenius equation ?
The temperature
dependence of rate of a chemical reaction can be accurately explained by
Arrhenius equation. It was first proposed by Dutch chemist J.H.
Vant’s Hoff but Swedish chemist Arrhenius
provides its physical justification and interpretation.
Where
K=
Rate constant
A= Arrhenius constant or frequency
factor or pre exponential factor
R= Universal gas constant =25/3 joule
per mole per second
Ea= Activation
Energy
T= temperature
-Ea/RT= Boltzmann factor or fraction of molecule having equal or greater
than Activation energy or fraction of molecule that have
kinetic energy greater than activation energy.
Related Questions:
(1) What is Arrhenius equation ?
(2) what happen when activation energy of a chemical reaction becomes equal to RT?
(3) What is the activation energy and how to different from threshold energy ?
(4) In Arrhenius equation for a certain reaction, the value of A and Ea (activation energy) are 4 × 10^13 sec–1 and 98.6 kJ mol–1 respectively. At what temperature, the reaction will have specific rate constant 1.1 × 10^–3 sec–1?
(5) The energy of activation for a reaction is 100 kJ mol–1. Presence of a catalyst lowers the energy of activation by 75%.What will be effect on rate of reaction at 20ºC, other things being equal?
(6) A drug becomes ineffective after 30 % decomposition. The original concentration of a sample was 5mg/mL which becomes 4.2 mg/mL during 20 months. Assuming the decomposition of first order , calculate the expiry time of the drug in months. What is the half life of the product?
(7) A first order reaction is 20 % completed in 10 minutes. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to go to 80 % completion.
(8) The rate of a reaction triple when temperature changes from 20”C to 50”C. Calculate energy of activation for the reaction (R = 8.314 JK^1 mol^1).
Friday, June 26, 2020
What is " Clasius Claperon" equation ?
What is "Anoxia" conditions ?
What is bends condition and what is relation of bends with Scuba divers ?
What is effect of temperature on vapour pressure ? Explain with CLASIUS CLAPERON equation.
What is vapour pressure and What is effect of temperature on vapour pressure ?
What are the Important structure information of Diamond?
Why are bridge head carbocations unstable?
According to Bredt's rule a bridgehead carbon atom of bicyclo compound cannot be sp2 hybridised or in other word a bridgehead carbon atom cannot be form double bond. unless the ring that contains at least eight atoms.
How does leaching of aluminium ore take place by Serpeck's process?
How does leaching of aluminium ore take place by Hall's process?
How does leaching of aluminium ore take place by Baeyer' process?
What are important ores of Aluminium ?
What are important ore of Iron ore ?
SN | Ores | Formula |
1 | Haematite (Red) | Fe2O3 |
2 | Magnetite | Fe3O4 |
3 | Siderite or Spathic | FeCO3 |
4 | Iron Pyrite (fool's Gold) | FeS2 |
5 | Goethite | FeO(OH) |
6 | Limonite | 2Fe3O4.3H2O |
Others Ores | ||
7 | Ilmenite (FeO+TiO2) | FeTiO3 |
8 | Chromite (FeO+Cr2O3) | FeCr2O4 |
What is composition of Wrought Iron ?
What is composition of Grey Cast Iron ?
What is composition of White cast iron ?
What are the composition of pig iron?.
SN | Impurities | % |
1 | Carbon (C) | 3- 4.3 |
2 | Silicon (Si) | 1-2.0 |
3 | Manganese (Mn) | 0.5-2.0 |
4 | Phosphorous (P) | 0.05-2.0 |
5 | Sulphure (S) | 0.05-1.0 |
Why density of water is greater than ice ?
Ice
and water both contains H2O molecules but in water H2O
molecules are more compactly arrange than in ice.
Ice
has a hexagonal cage like structure, inside it H2O
molecules are not closely packed.hence there is more vacant
space between the molecules of ice. As a result the volume
increases due to the vacant spaces. As a result density of ice
decrease.
Other
hand,On increasing temperature then kinetic energy of molecules increases as
result the interaction between the molecules decrease and as a result the the
molecules come closer to each other and the volume decreases, so the density
increases.
The density of water is maximum at 3.98 ℃ approximately 4 degree celsius.
What is the temperature at density of water is maximum ?
Why ice floats on water at room temperature ?
What is the temperature at density of water is maximum ?
Thursday, June 25, 2020
What is synergic bonding ?
How to find number of isomers of a octahedral complex containing all different ligands for example ML2,L2,L3,L4,L5,L6 type ?
Let us consider a octahedral complexes [ML1L2L3L4L5L5] where M is the central metal atom while L2, L2, L3 .... are six different ligands we shall represent the ligands by smallcase letters a,b,c etc. and the metal by M. We can write 12"cis" isomers in which ligands are separated by at angle 90° and 3 "trans" isomers in which ligands are separated by 180°.
The geometrical isomers of Mabcdef areas follows.
M(L1)(L2)(L3) (L4)(L5)(L6):
"Cis" isomers: separated by 90°
(1,2)(1,3)(1,4)(1,5)
(2,3)(3,4)(4,5)(5,2)
(2,6)(3,6)(4,6)(5,6)
"Trans " isomers: separated by 180°
(1,6)(2,4)(3,5)
What are necessary and sufficient conditions for coordination complex to show "optical isomerism"?
What are condition for geometrical isomerism in coordination compounds?
What is the temperature at density of water is maximum ?
Arrange the silicon halides into decreasing order of Lewis acids Character? SiF3, SiCl3, SiBr3, SiI3
What is d-orbital resonance?
It is a phenomenon in which electrons of ms and np get delocalized to vacant nd orbital because this availability of vacant d orbital to expect back bond get reduced .
In those molecules species where d orbital’s resonance exist of back Bonding is decreased.
What is conditions for back bonding ?
BCl3 ,BBr3 BI3 and B(Me)3 are electron deficient but do not undergo dimerization why ?
Why some compounds are undergoes dimerization ?
Tuesday, June 23, 2020
How do you calculate the number of all possible structural isomers for alkanes?
Yes we can find all possible structural isomers Of a given hydrocarbon.
Number of total structural isomers = 2^(N-4)+1
Where N is number of carbons in hydrocarbon
Example: (1)
Number of structural somers of butane (C4H10) is
SOLUTION:
Where , n=4
=2^(4-4)+1
=2^(0)+1
=1+1
=2
Example: (2)
Number of structural somers of butane (C5H12) is.
SOLUTION:
Where , n=5
=2^(5-4)+1
=2^(1)+1
=2+1
=3
Example: (3)
Number of structural somers of butane (C6H14) is.
SOLUTION:
Where , n=6
=2^(6-4)+1
=2^(2)+1
=4+1
=5
Example: (4)
Number of structural somers of butane (C7H16) is.
SOLUTION:
Where , n=7
=2^(7-4)+1
=2^(3)+1
=8+1
=9
Example: (5)
Number of structural somers of butane (C8H18) is.
SOLUTION:
Where , n=8
=2^(8-4)+1
=2^(4)+1
=16+1
=17
Example: (5)
Number of structural somers of butane (C8H18) is.
SOLUTION:
Where , n=9
=2^(9-4)+1
=2^(5)+1
=32+1
=33
How to find number of stereoisomers in a large compound (polyenes) containing double bonds?
What is denticity of NO and NO+ ligands ?
Monday, June 22, 2020
What is water in oil emulsions ? explain with examples.
What are Oil in water emulsions ? explain with examples.
Sunday, June 21, 2020
How many 3c-2e bonds and 3c-4e are there in Al2(CH3) 6?
Why are all P-Cl bond lengths equal in PCl3 but different in PCl5?
We know that in TBP, there is two type of bond present I.e. axial (longitudinal) and equatorial bond. Bond length of axial bond is longer (coordinate bond ) while equatorial bond is shorter due to covalent nature ( formed by overlapping of atomic orbitals).