Search This Blog
Tuesday, December 31, 2019
Are all the five bonds of PCl5 equivalent? Justify your answer.
Monday, December 30, 2019
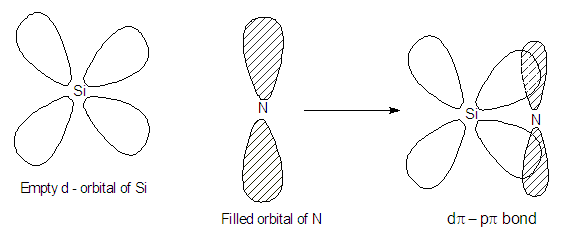
Silianol (SiH3OH) is more acidic than methanol (CH3OH) why?
Related Questions:
(1) Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
(2) Why Ga has small size than Al exceptionally
(3) Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
(4) What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
(5) What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
(6) Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
(7) Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
(8) Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
(9) Why B-F do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
(10) Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
(11) Why Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
Trisilyl amine, N(SiH3)3 is planar whereas trimethyl amines N(CH3)3 is pyramidal. Explain why?.
What is the molecular formula of Borax ?
Three-center four-electron Bridge bond (3C-4e Bond): Structure of AlCl3:
Related Questions:
(1) Why aqueous solution of AlCl3 is acidic in nature ?
(2) What happen when aq AlCl3 react with Acid or Base?
(3) Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
(4) Why BF3 do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
(5) Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
(6) B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter than B-F bond length in (BF4)- why?
(8) What is product of reaction between diborane (B2H6) and ammmonia (NH3)?
(9) Why methylation of Diborane (B2H6) replace four hydrogen only ?
(10) What is Use of Boric Acid?
(11) What is use of Orthoboric acids?
(12) What is basicity of "Boric acid" ?
(13) Why Boric acid exist in solid state ?
(14) What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
(15) What is effect of heat on Borax?
(16) What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
(17) What is the Sodium per borate ,give the structure and its uses?
(18) Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
(19) What is the molecular formula of Borax ?
(20) Why Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
(21) Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
(22) Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
(23) Four-center two-electron bond (4C-2e Bond): Structure of AlCl3:
(24) What is the difference between the structure of AlCl3 and diborane?