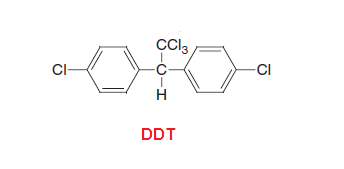
DDT,
the abbreviation for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, is a colorless,
tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochlorine. DDT use as pesticide and also called “miraculous”
by Winston Churchill because of the many lives it saved by killing disease carrying
mosquitoes.
DDT
was first synthesized in 1874 by the Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler.
DDT's insecticidal action was discovered by the Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller in 1939. DDT was used in the second half
of World War II to control malaria and typhus among civilians and troops. DDT
use is now banned in the United States and many developed countries because it
is a nonspecific insecticide that persists in the environment