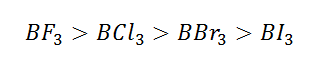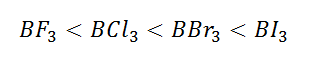Search This Blog
Monday, December 21, 2020
Why trimethylamine amine ( N(CH3)3) is tetrahedral while trisilyl amine (N(SiH3)3) planner.?
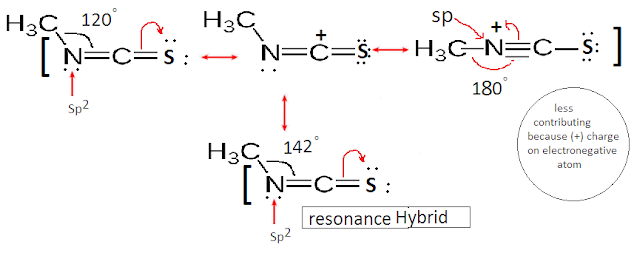
What is the Si–N–C bond angle in Silyl isothiocyanate and methyl isothiocyanate (H3CNCS)?
The hybridization of Nitrogen in Methyl isothiocyanate (H3CNCS) is Sp2. Thus bond angle (< C-N-C) is expected to be 120°. But it is slightly greater than 120° due to resonating structure. The resonating structure has N as Sp hybridized. Hence bond angle of the overall structure is found to be about 142°
But in case Silyl isothiocyanate (SiH3NCO), the structure is found to be (sp hybridized)
What are the order of extent back bonding, Lewis acid character and nucleophilicity of (BF3, BCl3, BBr3, BI3)boron trihalides?
(1) Back bonding extent in boron tri halides decreases from
BF3 to BI3 because on increasing of size of
p-orbital of halogens atom the strength of back bond decreases thus extent of back bonding:
Hence it is clear that BF3 is weakest Lewis acid
due to stronger 2pπ-2pπ back bonding (stronger partial double bond character)
in BF3 (lone pair orbital of fluorine into vacant orbital of
boron) and consequently behaves as less electron deficient. The back bonding
gradually decreases (From BF3 to BI3) and becomes
weakest in BI3. So that BI3 become strong Lewis acid
(3) The nucleophilicity(affinity towards nucleophile/water) order is
inversely proportional to the Lewis acid character thus
the nucleophilicity order is:
Related Questions:
Why aqueous solution of AlCl3 is acidic in nature ?
What happen when aq AlCl3 react with Acid or Base?
Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
Why BF3 do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter than B-F bond length in (BF4)- why?
What is product of reaction between diborane (B2H6) and ammmonia (NH3)?
Why methylation of Diborane (B2H6) replace four hydrogen only ?
What is use of Orthoboric acids?
What is basicity of "Boric acid" ?
Why Boric acid exist in solid state ?
What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
What is effect of heat on Borax?
What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
What is the Sodium per borate ,give the structure and its uses?
Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
What is the molecular formula of Borax ?
Why Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
Four-center two-electron bond (4C-2e Bond): Structure of AlCl3:
What are the conditions for Back bonding?
(1) Both of the atoms bonded with back Bonding are must be present in 2nd-2nd or 2nd-3rd period.
(2) One of the atoms has lone pair
and another have vacant Orbital and direction of back Bonding depends upon
vacant Orbital.
(3) The donor atom must
have localized donatable electron pair. In general these are later half second
period P - block elements (F, O, N and C).
(4) The acceptor atom must
have low energy empty orbital which generally are np or nd orbitals. Small and
similar sized orbital’s favour overlap.
EFFECTS OF BACK BONDING:
(1) It always leads to an
increase in bond order between the participating atoms.
(2) It always leads to an
increase in bond strength between participating atoms.
(3) It always leads to a
decrease in bond length between participating atoms.
What is the Back Bonding?
(1) Back bonding is a type of weaker π bond which is formed by sideways overlapping of filled orbital with empty orbital present on adjacent bonded atoms in a molecule.
(2) It is also considered as intermolecular Lewis acid-base interaction as it is a π bond.
(3) Back bonding is found to be effective and considerable in following type of overlapping.