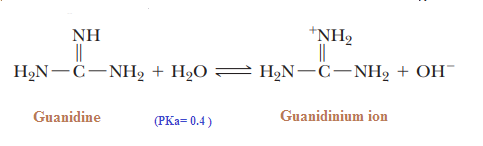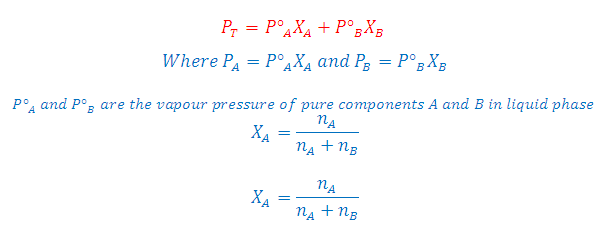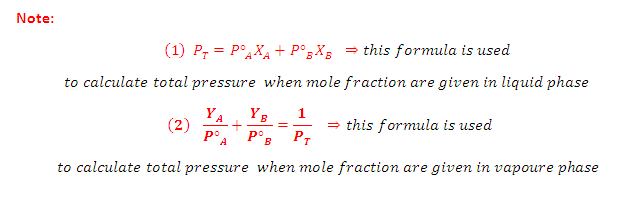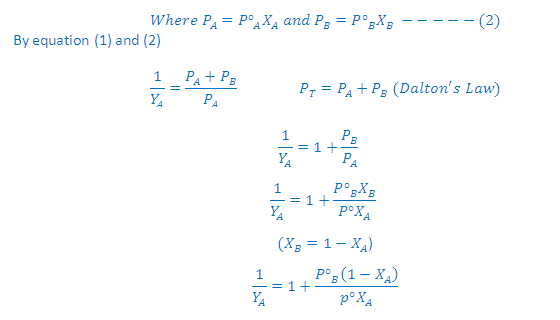Search This Blog
Sunday, May 31, 2020
Why The phenoxide ion is more stable than phenol ?
Which is more stable? CH3-CH2+ (Ethyl carbocation) or CH2=CH+ (Vinyl carbocation)? And why?
But in case of CH2=CH+. The two carbon atoms involved are sp2 hybridised. An sp2 hybridised carbon atom is more electronegative which increases positive charge and increases as the s-character of a hybridised carbon atom increases. As the the result inductive effect decreases by the neighbouring carbon atom.
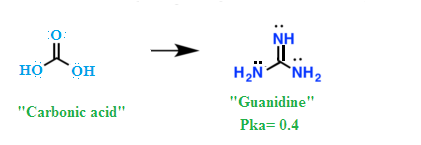
Why Guanidine behave as the strongest base among neutral compounds?. explaine the remarkable basicity of guanidine.
What is Guanidine and its structure , name amino acid which contains guanidine group ?
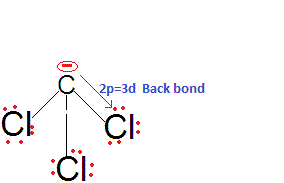
What is correct acidic strengths order of the haloforms acids ? Give correct explanation.
CF3-, CCl3-, CBr3- CI3-
We are expecting the acidic strength haloform acids asCHF3, CHCl3, CHBr3, CHI3 in decreasing order. Because Fluorine is most electronegative atom so it would be stabilize CF3- more, as electronegativity decreases from F to I the stability of conjugate -ve ion would be but that is not correct the actual order isCHCl3 > CHF3 > CHBr3 > CHI3.
This is because there is effective back bonding in CCl3-and hence the negative charge partially gets stabilised by back donation to the vacant 3d orbitals of Cl. Thus, CHCl3 is a stronger acid than CHF3 and also among them due to 2pπ-3dπ back bonding.
Saturday, May 30, 2020
Why are bridge head carbocations unstable?
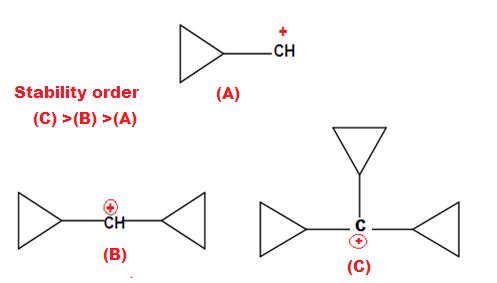
Why is cyclopropyl methyl carbocation exceptionally stable?
Friday, May 29, 2020
Azabicyclo[2,2,1]heptane is more basic thantriethylamine why?.
Which carbocation is more stable : Benzyl or Tertiary?
Actually answers of this question is always confusing, most of the authors believe benzyl carbocation is more stable than tertiary because benzyl carbocation involves in resonance.
But some of the authors believe that Tertiary carbocation is more stable as it involves maximum +I effect and maximum hyperconjuation +H (9-alpha hydrogens). Maximum +I and +H is more dominant than +M effect. Thus tertiary carbocation is more stable than benzyl carbocation.
Important note:
Stability of Benzyl , allylic and tertiary alkyl carbocation is practically almost same .so that stabilities infact cannot be compared.
Similar Questions:Tuesday, May 26, 2020
100 g of C6H12O6, (aq.) solution has vapour pressure is equal to 40 torr at certain temperature. Vapour pressre d H20(l) is 40.8 torr at same temperature if this solution is cooled to -0.93°C, what mass of ice wil be seperated out ? ( Kf :1.86 kg mol-1)
Molality of an aqueous solution of glucose (Molar mass :180 gmol-1) is 1.0 m. 590 g of this solution is cooled and the temperature is kept at -30°C. The amount of ice separated out (Kf for water 2 K kgmol-1) is...
Monday, May 25, 2020
Sunday, May 24, 2020
Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
Related Questions:
Why Ga has small size than Al exceptionally
Why aqueous solution of borax reacts with two moles of acids ?
What is structure of solid Ortho Boric acid ?
What is the structure of trimetaboric acid and trimetaborate ion?
Why Borazine is more reactive than benzene towards Electrophic Aromatic substitution reactions ?
Why Borazine (B3N3H6) is also known as inorganic benzene ?.
Why B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter (130 pm) than B-F bond Iength in BF4- (143 pm)?. Explain.
Why B-F do not exist as dimer?. Explain.
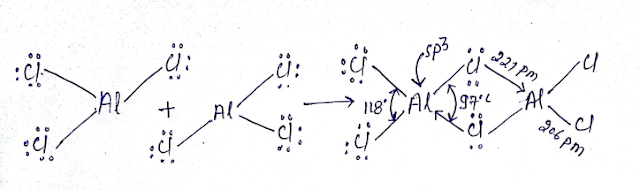
Although anhydrous aluminium chloride is covalent but its aqueous solution is ionic in nature. Why?
Why
Boric acid become strong acid in the presence of cis 1,2-diol or 1,3-diol ?
Why the C-C bond length in graphite is shorter than C-C bond length of diamond?
Graphite has carbon in sp2 hybrid state (33.3 % s character) but diamond has carbon in sp3 hybrid state (25 % s characrer). More is the percentage of s characters, (by Bent rule) more is the bond multiplicity and hence, shorter the bond is. Thus carbon-carban bond in graphite has double bond character but has a single bond character in diamond. Hence, C-C bond length in graphite is shorter than than in diamond.
Silianol (SiH3OH) is more acidic than methanol (CH3OH) why?
We know that acidic strength of an acid also depend upon stability of its conjugate base. So silianol is more acidic than methanol (H3C-OH) because conjugate base silianol (H3Si-OH) stablised by dispersal of negative charge in H3Si-O- ion by 2pπ—3dπ back bonding
Why Bond angle of NF3(102 degree) is lesser than in NH3 (107) ? explaine.
Explain C-H bond length of CH4 is longer than C-H bond length of Difloromethan (CH2F2) ?
Which is more acidic Me3C-OH Or Me3Si-OH and why ?
B-F bond length in BF3 is shorter than B-F bond length in (BF4)- why?
Dipole moment of PCl3F2 and P(CH3)3(CF)2 molecules are zero while dipole moment of PCl2F3 and P(CH3)2(CF3)3 are non zero why?
According to bent rule more electronegative atom or group attached those hybrids orbital have minimum S- character.
There is in trigonal bipiramidal (TBP) Geometry we known that axial orbital hare no s-character so F and -CF3 group are attached with equatorial positions. Hence dipole moment of P(CH3)2(CF3)2 is zero. While in case of PCl2F3 and P(CH3)2(CF)3 molecules one of the F and –CF3 group are also present at equatorial position hence there is net dipole moment.
Related Questions:
What is Bent’s
rule of hybridization?
Which of the
following compound have longest (S=O)bond length , O=SF2, O=SCl2, O=SBr2.
Why Bond length
of O-O is greater in H2O2 than O2F2?
How to arrange
increasing (C-H) bond length in increasing order and H-C-F bond angle in the
given compounds, CH4, CH3F, CH2F2 and CHF3 ?
Dipole moment of
PCl3F2 molecule is zero while dipole moment of PCl2F3 molecule is non zero why?
Dipole moment of
P(CH3)2(CF3)2 molecule is zero while dipole moment of P(CH3)2(CF)3 molecule is
non zero why?
Dipole moment of PCl2F3 is non zero while dipole moment of PCl3F2 is zero why?
What is Banana bond (3C-2e bridge bond) ? Explaine with suitable examples.
What is bridge bond ? explaine 3C-4e bridge bond with suitable examples .
If silver iodide crystallizes in a zinc blende structure with I- ions forming the lattice then calculate fraction of the tetrahedral voids occupied by Ag+ ions.
Arrange the silicon halides into decreasing order of Lewis acids Character? SiF3, SiCl3, SiBr3, SiI3
What is the d-Orbital resonance ?
It is a phenomenon in which electrons of ms and np get delocalized to vacant nd orbital because this availability of vacant d orbital to expect back bond get reduced .
In those molecules species where d orbital’s resonance exist of back Bonding is decreased.
N(CH3)3 is pyramidal while(SiH3)3N is trigonal planer why?
Which of the following pair of solution (aq.) contain isotonic solution at same temperature? (Assume 100 % ionisation of electrolytes) (1) 0.1 M NaCI and 0.2 M CaCI2(2) 0.1 M NaCI and 0.3 M AICI3 (3) 0.3 M NaCI and 0.1 M AICI3 (4) 0.3 M NaCI and 0.2 CaCI2
Freezing point of pure liquid A is T K. If some amount of non-electrolyte non-volatile impurity is added in A, an ideal solution is formed. On cooling at 200 K, only 30% (by mass) liquid A is present and at 201 K, 60 % (by mass) liquid A is present. The value of T is .
Liquid A and B form ideal solution at temperature T. Mole fraction of A in liquid and vapour phase are 0.4 and 4/13 respectively, when total pressure is 130 torr. The vapour pressure (in torr) of A and B in pure state at temperature T are respectively.
What is the relation between Raoult' law and Dalton's ?
Saturday, May 23, 2020
A metal crystallizes into two cubic phases, face centered cubic (fcc) and body centered cubic (bcc), whose unit cell lengths are 3.5 A° and 3.0 A°, rcspcctively. Calculate the ratio of densities of fcc and bcc. (IIT-JEE 1999)
A metallic element crystallizes into a lattice containing a sequence of layers ABABAB....Any packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What percentage by volume of this lattice is empty space? ( IIT-.IEF 2006)
The coordination number of Al in the crystalline state of AlCl3 is .... (IIT-JEE 2009)
The number of hexagonal faces that are present in truncated octahedron is .... (IIT-JEE 2011)
What are structural information of Dimomd ?
Diamond structure
is ZnS type structure in which carbon
atoms forms a face centred cubic (FCC/CCP) lattice
as well as four out of eight
(50%) or alternate tetrahedral voids are
occupied by carbon atoms. Every atom in this structure is surrounded
tetrahedrally by four other. No discrete molecule can be discerned (identified)
in diamond .the entire crystal is giant molecule a unit cell of which is shown
as below.
Note
: Only those atoms which
form four covalent bond produce a repeated 3D structure using only covalent
bonds.
Lattice of Diamond is ZnS type structure.
(1) C- form FCC/CCP (4-atoms)
(2) C- atoms present at the (50%) alternative
tetrahedral voids (4-atoms)
(3) Total Number of one lattice unit is
eight (8) hence molecular formula of diamond is (C8) (i.e. Z= 8)
(4) Number of C-C bond in lattice cell
is = 4×4= 16
(5) Number of C-C bond per carbon atom
is 16/8=2
(6) The distance between two Corbin atom is dC-C = a√3/4 and the radius of carbon atom = dc-c/2 = rc = a√3/2x4
(8) Packing efficiency (PE = π√3/10= 0.34 or 34%):
(9) Voids = 66 %
Additional
Information:
Related Questions:
What are the normal spinel structures?
What are the inverse spinel structures?
How to calculate radius ratio of square Voids?
How to calculate radius ratio triangular voids?
How to calculate packing fraction or packing efficiency of two dimensional (2D) hexagonal packing solid atoms?
The coordination number of Al in the crystalline state of AlCl3 is .... (IIT-JEE 2009)
The number of hexagonal faces that are present in truncated octahedron is .... (IIT-JEE 2011)
What are structural information of Dimomd ?
In diamond, carbon atoms occupy FCC/CCP lattice point as well as alternate tetrahedral voids. If edge length of unit cell is 3.56pm, the radius of carbon atom is ?
Friday, May 22, 2020
Decimolar solution of K4[Fe(CN)6] dissociate by 60% at 27°C. Determine osmotlc pressure in Nature/M2.
A complex is wrltten as M(en)y.xBr. lts 0.05 molar solution shows 2.46 atm osmotlc pressure at 27°C. Assuming 100 % ionisaton and coordination number of metal (iii) is six, complex may be:
A non Stoichiometric oxide of iron represented as Fe_x O_1.0 , contains one Fe+3 for every three Fe+2 ions , then find the value of x is...
What is Gold number of protective colloidal solution?
Lyophilic sols are more stable than lyophobic sols. Why ?
Give some examples of common negatively charged colloidal solution?
Give some examples of common positively charged colloidal solution?
Saturday, May 16, 2020
A mixture of weighing 228 g contain CaCl2 and NaCl . If this mixture is dissolved in 10 kg of water and form ideal solution that boil at 100.364 ℃ The mol % of NaCl in mixture is [ kb of water = 0.52 K per mol Kg]
NaCl and CaCl2 both are strong electrolytes hence Vant’s Hoff factor are 2 and 3 respectively.
Moles of NaCl =
x/58.5
Moles of CaCl2
= 228-x
And hence molality of
NaCl and CaCl2 are
Molality of NaCl =
×/58.5×10kg
Molality of CaCl2= 228-x/111×10kg
We know that
∆Tb = i1m1+i2m2
100.364= 2(×/58.5×10kg) +3(228-x/111×10kg)
On solving we got x=
117 g
Moles of NaCl=
117/58.5 =2
Moles of CaCl2= 111/111=1
Mole percentage (%)
0f NaCl = (2/2+1)x100= 66.67%
Related Questions: